MetaboAnalyst 2.0--a comprehensive server for metabolomic data analysis
- PMID: 22553367
- PMCID: PMC3394314
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks374
MetaboAnalyst 2.0--a comprehensive server for metabolomic data analysis
Abstract
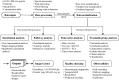
First released in 2009, MetaboAnalyst (www.metaboanalyst.ca) was a relatively simple web server designed to facilitate metabolomic data processing and statistical analysis. With continuing advances in metabolomics along with constant user feedback, it became clear that a substantial upgrade to the original server was necessary. MetaboAnalyst 2.0, which is the successor to MetaboAnalyst, represents just such an upgrade. MetaboAnalyst 2.0 now contains dozens of new features and functions including new procedures for data filtering, data editing and data normalization. It also supports multi-group data analysis, two-factor analysis as well as time-series data analysis. These new functions have also been supplemented with: (i) a quality-control module that allows users to evaluate their data quality before conducting any analysis, (ii) a functional enrichment analysis module that allows users to identify biologically meaningful patterns using metabolite set enrichment analysis and (iii) a metabolic pathway analysis module that allows users to perform pathway analysis and visualization for 15 different model organisms. In developing MetaboAnalyst 2.0 we have also substantially improved its graphical presentation tools. All images are now generated using anti-aliasing and are available over a range of resolutions, sizes and formats (PNG, TIFF, PDF, PostScript, or SVG). To improve its performance, MetaboAnalyst 2.0 is now hosted on a much more powerful server with substantially modified code to take advantage the server's multi-core CPUs for computationally intensive tasks. MetaboAnalyst 2.0 also maintains a collection of 50 or more FAQs and more than a dozen tutorials compiled from user queries and requests. A downloadable version of MetaboAnalyst 2.0, along detailed instructions for local installation is now available as well.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MetaboAnalyst 3.0--making metabolomics more meaningful.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jul 1;43(W1):W251-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv380. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25897128 Free PMC article.
-
MetaboAnalyst: a web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jul;37(Web Server issue):W652-60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp356. Epub 2009 May 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19429898 Free PMC article.
-
Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2019 Dec;68(1):e86. doi: 10.1002/cpbi.86. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31756036
-
Using MetaboAnalyst 3.0 for Comprehensive Metabolomics Data Analysis.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016 Sep 7;55:14.10.1-14.10.91. doi: 10.1002/cpbi.11. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27603023 Review.
-
Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Metabolomics Data Analysis, Interpretation, and Integration with Other Omics Data.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2104:337-360. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0239-3_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31953825 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical characterization, pathway enrichments and bioactive potentials of catechin-producing endophytic fungi isolated from tea leaves.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 21;14(45):33034-33047. doi: 10.1039/d4ra05758a. eCollection 2024 Oct 17. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39434990 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted Metabolomic Biomarker Discovery for the Detection of Ectopic Pregnancy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 26;25(19):10333. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910333. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408663 Free PMC article.
-
Specific activation of the integrated stress response uncovers regulation of central carbon metabolism and lipid droplet biogenesis.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 27;15(1):8301. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52538-5. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39333061 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring gut microbiota and metabolite alterations in patients with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy using high-throughput sequencing and untargeted metabolomics.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 29;15:1413890. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1413890. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39135625 Free PMC article.
-
Automated preparation of plasma lipids, metabolites, and proteins for LC/MS-based analysis of a high-fat diet in mice.J Lipid Res. 2024 Sep;65(9):100607. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2024.100607. Epub 2024 Jul 25. J Lipid Res. 2024. PMID: 39067520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weljie AM, Newton J, Mercier P, Carlson E, Slupsky CM. Targeted profiling: quantitative analysis of 1H NMR metabolomics data. Anal. Chem. 2006;78:4430–4442. - PubMed
-
- Dietmair S, Timmins NE, Gray PP, Nielsen LK, Kromer JO. Towards quantitative metabolomics of mammalian cells: development of a metabolite extraction protocol. Anal. Biochem. 2010;404:155–164. - PubMed
-
- Griffiths WJ, Koal T, Wang Y, Kohl M, Enot DP, Deigner HP. Targeted metabolomics for biomarker discovery. Angewandte Chemie. 2010;49:5426–5445. - PubMed
-
- Ewald JC, Heux S, Zamboni N. High-throughput quantitative metabolomics: workflow for cultivation, quenching, and analysis of yeast in a multiwell format. Anal. Chem. 2009;81:3623–3629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

