MicroRNAs miR-125a and miR-125b constitutively activate the NF-κB pathway by targeting the tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3, A20)
- PMID: 22550173
- PMCID: PMC3356650
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1200081109
MicroRNAs miR-125a and miR-125b constitutively activate the NF-κB pathway by targeting the tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3, A20)
Abstract
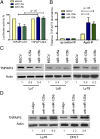
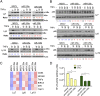
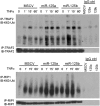
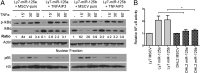
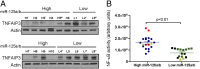
Constitutive activation of the NF-κB pathway is associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) pathogenesis, but whether microRNA dysfunction can contribute to these events remains unclear. Starting from an integrative screening strategy, we uncovered that the negative NF-κB regulator TNFAIP3 is a direct target of miR-125a and miR-125b, which are commonly gained and/or overexpressed in DLBCL. Ectopic expression of these microRNAs in multiple cell models enhanced K63-linked ubiquitination of proximal signaling complexes and elevated NF-κB activity, leading to aberrant expression of its transcriptional targets and the development of a proproliferative and antiapoptotic phenotype in malignant B cells. Concordantly, genetic inhibition of miR-125a/miR-125b blunted NF-κB signals, whereas rescue assays and genetic modulation of a TNFAIP3-null model defined the essential role of the TNFAIP3 targeting on miR-125a/miR-125b-mediated lymphomagenesis. Importantly, miR-125a/mir-125b effects on TNFAIP3 expression and NF-κB activity were confirmed in a well-characterized cohort of primary DLBCLs. Our data delineate a unique epigenetic model for aberrant activation of the NF-κB pathway in cancer and provide a coherent mechanism for the role of these miRNAs in immune cell activation and hematopoiesis. Further, as miR-125b is a direct NF-κB transcriptional target, our results suggest the presence of a positive self-regulatory loop whereby termination of TNFAIP3 function by miR-125 could strengthen and prolong NF-κB activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-125b controls apoptosis and temozolomide resistance by targeting TNFAIP3 and NKIRAS2 in glioblastomas.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jun 5;5(6):e1279. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.245. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24901050 Free PMC article.
-
miR-125b promotes the NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response in NAFLD via directly targeting TNFAIP3.Life Sci. 2021 Apr 1;270:119071. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119071. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33515562
-
miR-29 acts as a decoy in sarcomas to protect the tumor suppressor A20 mRNA from degradation by HuR.Sci Signal. 2013 Jul 30;6(286):ra63. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004177. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23901138 Free PMC article.
-
A20-mediated negative regulation of canonical NF-κB signaling pathway.Immunol Res. 2013 Dec;57(1-3):166-71. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8463-2. Immunol Res. 2013. PMID: 24242761 Review.
-
The ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 (TNFAIP3) is a central regulator of immunopathology.Trends Immunol. 2009 Aug;30(8):383-91. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2009.05.007. Epub 2009 Jul 28. Trends Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19643665 Review.
Cited by
-
mRNA and miRNA regulatory networks reflective of multi-walled carbon nanotube-induced lung inflammatory and fibrotic pathologies in mice.Toxicol Sci. 2015 Mar;144(1):51-64. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu262. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25527334 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation roles of miR-125b, miR-221 and miR-27b in porcine Salmonella infection signalling pathway.Biosci Rep. 2016 Aug 31;36(4):e00375. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160243. Print 2016 Aug. Biosci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27474500 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic screen reveals MicroRNA clusters that significantly regulate four major signaling pathways.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48474. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048474. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23144891 Free PMC article.
-
D2HGDH regulates alpha-ketoglutarate levels and dioxygenase function by modulating IDH2.Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 16;6:7768. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8768. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26178471 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Sensitizes TRAIL-Induced Hepatocyte Apoptosis by Inhibiting the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase A20.PLoS One. 2015 May 20;10(5):e0127329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127329. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25993287 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

