Links between metabolism and cancer
- PMID: 22549953
- PMCID: PMC3347786
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.189365.112
Links between metabolism and cancer
Abstract
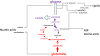
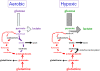
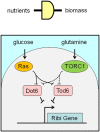
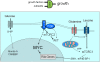
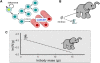
Metabolism generates oxygen radicals, which contribute to oncogenic mutations. Activated oncogenes and loss of tumor suppressors in turn alter metabolism and induce aerobic glycolysis. Aerobic glycolysis or the Warburg effect links the high rate of glucose fermentation to cancer. Together with glutamine, glucose via glycolysis provides the carbon skeletons, NADPH, and ATP to build new cancer cells, which persist in hypoxia that in turn rewires metabolic pathways for cell growth and survival. Excessive caloric intake is associated with an increased risk for cancers, while caloric restriction is protective, perhaps through clearance of mitochondria or mitophagy, thereby reducing oxidative stress. Hence, the links between metabolism and cancer are multifaceted, spanning from the low incidence of cancer in large mammals with low specific metabolic rates to altered cancer cell metabolism resulting from mutated enzymes or cancer genes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Warburg effect: essential part of metabolic reprogramming and central contributor to cancer progression.Int J Radiat Biol. 2019 Jul;95(7):912-919. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2019.1589653. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Int J Radiat Biol. 2019. PMID: 30822194 Review.
-
The control of the metabolic switch in cancers by oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes.Science. 2010 Dec 3;330(6009):1340-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1193494. Science. 2010. PMID: 21127244 Review.
-
Tumor microenvironment and metabolic synergy in breast cancers: critical importance of mitochondrial fuels and function.Semin Oncol. 2014 Apr;41(2):195-216. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Semin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24787293 Review.
-
MYC-induced cancer cell energy metabolism and therapeutic opportunities.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Nov 1;15(21):6479-83. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-0889. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19861459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Metabolic Reprogramming in Cancer Cells Supporting Enhanced Growth and Proliferation.Cells. 2021 Apr 29;10(5):1056. doi: 10.3390/cells10051056. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33946927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sirtuins and the Metabolic Hurdles in Cancer.Curr Biol. 2015 Jun 29;25(13):R569-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.05.012. Curr Biol. 2015. PMID: 26126285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Starving cancer from the outside and inside: separate and combined effects of calorie restriction and autophagy inhibition on Ras-driven tumors.Cancer Metab. 2016 Sep 16;4:18. doi: 10.1186/s40170-016-0158-4. eCollection 2016. Cancer Metab. 2016. PMID: 27651895 Free PMC article.
-
MUC16-mediated activation of mTOR and c-Myc reprograms pancreatic cancer metabolism.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 7;6(22):19118-31. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4078. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26046375 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Dependencies in RAS-Driven Cancers.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Apr 15;21(8):1828-34. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2425. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25878364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profiling cellular bioenergetics, glutathione levels, and caspase activities in stomach biopsies of patients with upper gastrointestinal symptoms.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan 14;21(2):644-52. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.644. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25593494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bello-Fernandez C, Cleveland JL 1992. c-myc transactivates the ornithine decarboxylase gene. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 182: 445–452 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
