Down-regulation of KRAS-interacting miRNA-143 predicts poor prognosis but not response to EGFR-targeted agents in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 22549179
- PMCID: PMC3364114
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.175
Down-regulation of KRAS-interacting miRNA-143 predicts poor prognosis but not response to EGFR-targeted agents in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: MicroRNA-143 (miRNA-143) is frequently down-regulated in colorectal cancer (CRC) and may influence CRC cell proliferation, apoptosis and sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil. mRNA encoded by the KRAS oncogene has been identified as a target of miRNA-143. However, the prognostic significance of miRNA-143 expression and the ability to predict patient response to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeted agents have not yet been explored.
Methods: We examined 77 CRC patients who were identified by pyrosequencing to have wild-type KRAS and were subsequently treated with EGFR-targeted therapy with the monoclonal antibodies cetuximab or panitumumab. MicroRNA-143 expression was measured in CRC tissue and corresponding non-neoplastic colon tissue by RT-PCR and its expression level was correlated with clinico-pathological characteristics. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to calculate cancer-specific survival (CSS). The progression-free survival (PFS) and objective response rates on EGFR-targeted therapy were also evaluated.
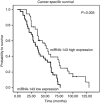
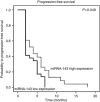
Results: Down-regulation of miRNA-143 was observed in 47 out of 77 (61%) tumours. Multivariate Cox regression analysis identified low levels of miRNA-143 expression as an independent prognostic factor with respect to CSS (hazard ratio=1.92, confidence interval=1.1-3.4, P=0.024). A significant difference was also observed with regard to PFS on EGFR-targeted therapy (P=0.031), but there were no significant differences with regard to the objective response rates.
Conclusion: Our data indicate that miRNA-143 expression levels serve as an independent prognostic biomarker for CRC in KRAS wild-type patients. No role for miRNA-143 expression as a predictive biomarker for EGFR-targeted agents could be identified. Given its negative impact on CSS and PFS, miRNA-143 represents a novel prognosticator and a promising drug target for patients with CRC.
© 2012 Cancer Research UK
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-181a is associated with poor clinical outcome in patients with colorectal cancer treated with EGFR inhibitor.J Clin Pathol. 2014 Mar;67(3):198-203. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2013-201904. Epub 2013 Oct 4. J Clin Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24098024
-
PTEN gene expression and mutations in the PIK3CA gene as predictors of clinical benefit to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody therapy in patients with KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2012 Jun;11(2):143-50. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2011.12.001. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22285706 Free PMC article.
-
Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Dec 10;26(35):5705-12. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.0786. Epub 2008 Nov 10. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 19001320
-
Extended RAS mutations and anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody survival benefit in metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials.Ann Oncol. 2015 Jan;26(1):13-21. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu378. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Ann Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25115304 Review.
-
PIK3CA exon 20 mutations as a potential biomarker for resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Oncol. 2012 Jun;23(6):1518-25. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdr464. Epub 2011 Oct 29. Ann Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22039088 Review.
Cited by
-
From small to big: microRNAs as new players in medulloblastomas.Tumour Biol. 2013 Feb;34(1):9-15. doi: 10.1007/s13277-012-0579-9. Epub 2012 Nov 25. Tumour Biol. 2013. PMID: 23179395 Review.
-
The role of microRNAs in breast cancer stem cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jul 15;14(7):14712-23. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714712. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23860207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulated microRNAs in the colorectal cancer: diagnostic and therapeutic perspectives.BMB Rep. 2018 Nov;51(11):563-571. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2018.51.11.116. BMB Rep. 2018. PMID: 30158023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic significance of microRNA-16 expression in human colorectal cancer.World J Surg. 2013 Dec;37(12):2944-9. doi: 10.1007/s00268-013-2205-4. World J Surg. 2013. PMID: 24045965
-
The influence of FCGR2A and FCGR3A polymorphisms on the survival of patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell head and neck cancer treated with cetuximab.Pharmacogenomics J. 2018 May 22;18(3):474-479. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2017.37. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Pharmacogenomics J. 2018. PMID: 28719596
References
-
- Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ, Juan T, Sikorski R, Suggs S, Radinsky R, Patterson SD, Chang DD (2008) Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(10): 1626–1634 - PubMed
-
- Bardelli A, Siena S (2010) Molecular mechanisms of resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(7): 1254–1261 - PubMed
-
- Borralho PM, Kren BT, Castro RE, da Silva IB, Steer CJ, Rodrigues CM (2009) MicroRNA-143 reduces viability and increases sensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in HCT116 human colorectal cancer cells. FEBS J 276(22): 6689–6700 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous