Multiple dynamic representations in the motor cortex during sensorimotor learning
- PMID: 22538608
- PMCID: PMC4601999
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11039
Multiple dynamic representations in the motor cortex during sensorimotor learning
Abstract
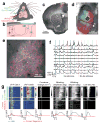
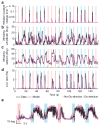
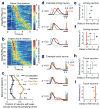
The mechanisms linking sensation and action during learning are poorly understood. Layer 2/3 neurons in the motor cortex might participate in sensorimotor integration and learning; they receive input from sensory cortex and excite deep layer neurons, which control movement. Here we imaged activity in the same set of layer 2/3 neurons in the motor cortex over weeks, while mice learned to detect objects with their whiskers and report detection with licking. Spatially intermingled neurons represented sensory (touch) and motor behaviours (whisker movements and licking). With learning, the population-level representation of task-related licking strengthened. In trained mice, population-level representations were redundant and stable, despite dynamism of single-neuron representations. The activity of a subpopulation of neurons was consistent with touch driving licking behaviour. Our results suggest that ensembles of motor cortex neurons couple sensory input to multiple, related motor programs during learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests
Figures



Similar articles
-
Learning-related fine-scale specificity imaged in motor cortex circuits of behaving mice.Nature. 2010 Apr 22;464(7292):1182-6. doi: 10.1038/nature08897. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20376005
-
Pathway-specific reorganization of projection neurons in somatosensory cortex during learning.Nat Neurosci. 2015 Aug;18(8):1101-8. doi: 10.1038/nn.4046. Epub 2015 Jun 22. Nat Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26098757
-
Activity in motor-sensory projections reveals distributed coding in somatosensation.Nature. 2012 Sep 13;489(7415):299-303. doi: 10.1038/nature11321. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22922646 Free PMC article.
-
Intracortical processes regulating the integration of sensory information.Prog Brain Res. 1990;86:129-41. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63172-6. Prog Brain Res. 1990. PMID: 1982365 Review.
-
Learning from learning: what can visuomotor adaptations tell us about the neuronal representation of movement?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;629:221-42. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-77064-2_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 19227502 Review.
Cited by
-
Cortical neural responses to previous trial outcome during learning of a directional choice task.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Apr 1;113(7):1963-76. doi: 10.1152/jn.00238.2014. Epub 2014 Dec 31. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25552636 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and structural underpinnings of neuronal assembly formation in learning.Nat Neurosci. 2016 Dec;19(12):1553-1562. doi: 10.1038/nn.4418. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Nat Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27749830 Review.
-
Contemporary approaches to neural circuit manipulation and mapping: focus on reward and addiction.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Sep 19;370(1677):20140210. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0210. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26240425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Learning, Motivation, and Visual Perception in Five Transgenic Mouse Lines Expressing GCaMP in Distinct Cell Populations.Front Behav Neurosci. 2020 Jun 23;14:104. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.00104. eCollection 2020. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32655383 Free PMC article.
-
Stable task information from an unstable neural population.Elife. 2020 Jul 14;9:e51121. doi: 10.7554/eLife.51121. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32660692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wise SP, Moody SL, Blomstrom KJ, Mitz AR. Changes in motor cortical activity during visuomotor adaptation. Experimental brain research. Experimentelle Hirnforschung. Experimentation cerebrale. 1998;121:285–299. - PubMed
-
- Komiyama T, et al. Learning-related fine-scale specificity imaged in motor cortex circuits of behaving mice. Nature. 2010;464:1182–1186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

