Comparison of postoperative pain and satisfaction after dacryocystorhinostomy in patients operated on under local and general anesthesia
- PMID: 22534704
- PMCID: PMC3560633
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.882730
Comparison of postoperative pain and satisfaction after dacryocystorhinostomy in patients operated on under local and general anesthesia
Abstract
Background: There has been only 1 study on postoperative pain after external dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) that compared pain between 2 groups of patients; 1 group received local anesthesia and the other received general anesthesia. To further characterize the relationship between these 2 types of anesthesia and postoperative pain, we designed a study in which a single patient received these 2 different anesthesia modalities for a short interval on 2 different sides.
Material/methods: There were 50 participants in this study. External DCR was performed on the same participant on both sides using local anesthesia on 1 side and general anesthesia on the other. Postoperative pain was measured using the visual analogue scale (VAS), and localization and timing of pain were reported by the participants. Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) were documented if present.
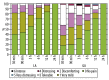
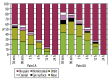
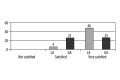
Results: Pain levels were significantly higher with general anesthesia 3 hours post-surgery, and 6 hours post-surgery the pain remains higher following general anesthesia but is borderline insignificant (p=0.051). However, 12 hours post-surgery, there is no significant difference in the pain level (p=0.240). There was no significant difference in the localization of pain with local and general anesthesia. Postoperative nausea is significantly more frequent after general anesthesia, and vomiting only occurs with general anesthesia. Local anesthesia was preferred by 94% of the participants (47 out of 50).
Conclusions: The vast majority of patients in our study who have undergone both GA and LA DCR would choose LA again, providing a compelling case for use of the LA technique.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Randomised, masked study of local anaesthesia administered prior to external dacryocystorhinostomy under general anaesthesia.Eye (Lond). 2019 Mar;33(3):374-379. doi: 10.1038/s41433-018-0201-5. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Eye (Lond). 2019. PMID: 30228368 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Local versus general anesthesia for external dacryocystorhinostomy in young patients.Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005 May;21(3):201-6. doi: 10.1097/01.iop.0000163317.73873.c9. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005. PMID: 15942495 Clinical Trial.
-
[Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) under local anesthesia].Harefuah. 2015 Feb;154(2):110-3, 136, 135. Harefuah. 2015. PMID: 25856864 Hebrew.
-
Intraoperative local anaesthesia for reduction of postoperative pain following general anaesthesia for dental treatment in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Dec 23;2014(12):CD009742. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009742.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25532729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inguinal hernia repair: anaesthesia, pain and convalescence.Dan Med Bull. 2003 Aug;50(3):203-18. Dan Med Bull. 2003. PMID: 13677240 Review.
Cited by
-
Outcomes of External Dacryocystorhinostomy under General and Local Anesthetics in a Tertiary Clinic.Beyoglu Eye J. 2022 Feb 18;7(1):25-29. doi: 10.14744/bej.2021.95967. eCollection 2022. Beyoglu Eye J. 2022. PMID: 35265798 Free PMC article.
-
Analgesic Efficacy of Pre-operative Pregabalin in Dacryocystorhinostomy Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials.Cureus. 2023 Nov 13;15(11):e48720. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48720. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38024096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patients undergoing dacryocystorhinostomy surgery in northern iran: an epidemiologic study.Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2014 May;4(3):365-8. doi: 10.4103/2141-9248.133461. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2014. PMID: 24971210 Free PMC article.
-
Randomised, masked study of local anaesthesia administered prior to external dacryocystorhinostomy under general anaesthesia.Eye (Lond). 2019 Mar;33(3):374-379. doi: 10.1038/s41433-018-0201-5. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Eye (Lond). 2019. PMID: 30228368 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of spinal and general anesthesia on the metabolic, hormonal, and hemodynamic response in elective surgical patients.Med Sci Monit. 2014 Oct 6;20:1833-40. doi: 10.12659/MSM.890981. Med Sci Monit. 2014. PMID: 25284266 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Hughes SM. The History of Lacrimal Surgery. Adv Ophthal Plastic & Reconstruct Surgery. 1986;5:139–68. - PubMed
-
- Caesar RH, Mc Nab AA. External dacryocystorhinostomy and local anesthesia. Technique to measure minimized blood loss. Opthal Plast Reconst Surg. 2004;20:57–59. - PubMed
-
- Moore WMH, Bentley CR, Olver JM. Functional and anatomic results after two types of endoscopic endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy: surgical and holmium laser. Ophthalmology. 2002;109:1575–82. - PubMed
-
- Jordan DR. Avoiding blood loss in outpatient DCR. Opthal Plast Reconst Surg. 1991;7:261–66. - PubMed
-
- McNab AA, Simmie RJ. Effectiveness of local anesthesia for external dacryocystorhinostomy. Clin Experimental Ophthalmol. 2002;30:270–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources