Postmortem Interval Influences α-Synuclein Expression in Parkinson Disease Brain
- PMID: 22530163
- PMCID: PMC3317023
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/614212
Postmortem Interval Influences α-Synuclein Expression in Parkinson Disease Brain
Abstract
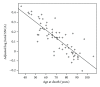
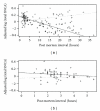
Duplications and triplications of the α-synuclein (SNCA) gene increase risk for PD, suggesting increased expression levels of the gene to be associated with increased PD risk. However, past SNCA expression studies in brain tissue report inconsistent results. We examined expression of the full-length SNCA transcript (140 amino acid protein isoform), as well as total SNCA mRNA levels in 165 frontal cortex samples (101 PD, 64 control) using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Additionally, we evaluated the relationship of eight SNPs in both 5' and 3' regions of SNCA with the gene expression levels. The association between postmortem interval (PMI) and SNCA expression was different for PD and control samples: SNCA expression decreased with increasing PMI in cases, while staying relatively constant in controls. For short PMI, SNCA expression was increased in PD relative to control samples, whereas for long PMI, SNCA expression in PD was decreased relative to control samples.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Levels of alpha-synuclein mRNA in sporadic Parkinson disease patients.Mov Disord. 2006 Oct;21(10):1703-8. doi: 10.1002/mds.21007. Mov Disord. 2006. PMID: 16795004
-
Transcript expression levels of full-length alpha-synuclein and its three alternatively spliced variants in Parkinson's disease brain regions and in a transgenic mouse model of alpha-synuclein overexpression.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2012 Feb;49(2):230-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2011.11.006. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22155155 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic regulation of alpha-synuclein mRNA expression in various human brain tissues.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 16;4(10):e7480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007480. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19834617 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants and animal models in SNCA and Parkinson disease.Ageing Res Rev. 2014 May;15:161-76. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Ageing Res Rev. 2014. PMID: 24768741 Review.
-
[Neurodegeneration and epigenetics].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2012 Nov;32(5-6):269-73. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 23373314 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-Targeted Gene Regulation in Salivary Gland Tissue of De Novo Parkinson's Disease Patients.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Apr;62(4):4591-4604. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04581-y. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39467986
-
Interpreting Gene Expression Effects of Disease-Associated Variants: A Lesson from SNCA rs356168.Front Genet. 2017 Sep 20;8:133. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00133. eCollection 2017. Front Genet. 2017. PMID: 28979294 Free PMC article.
-
Concordance analysis of microarray studies identifies representative gene expression changes in Parkinson's disease: a comparison of 33 human and animal studies.BMC Neurol. 2017 Mar 23;17(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12883-017-0838-x. BMC Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28335819 Free PMC article.
-
Acute increase of α-synuclein inhibits synaptic vesicle recycling evoked during intense stimulation.Mol Biol Cell. 2014 Dec 1;25(24):3926-41. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-02-0708. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Mol Biol Cell. 2014. PMID: 25273557 Free PMC article.
-
Transmission of Soluble and Insoluble α-Synuclein to Mice.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2015 Dec;74(12):1158-69. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000262. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26574670 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, et al. Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science. 1997;276(5321):2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Krüger R, Kuhn W, Müller T, et al. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nature Genetics. 1998;18(2):106–108. - PubMed
-
- Zarranz JJ, Alegre J, Gómez-Esteban JC, et al. The new mutation, E46K, of α-synuclein causes Parkinson and lewy body dementia. Annals of Neurology. 2004;55(2):164–173. - PubMed
-
- Singleton AB, Farrer M, Johnson J, et al. α-synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science. 2003;302(5646):p. 841. - PubMed
-
- Chartier-Harlin MC, Kachergus J, Roumier C, et al. α-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson’s disease. The Lancet. 2004;364(9440):1167–1169. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

