Mmi1 RNA surveillance machinery directs RNAi complex RITS to specific meiotic genes in fission yeast
- PMID: 22522705
- PMCID: PMC3364741
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.105
Mmi1 RNA surveillance machinery directs RNAi complex RITS to specific meiotic genes in fission yeast
Abstract
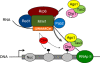
RNA interference (RNAi) silences gene expression by acting both at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels in a broad range of eukaryotes. In the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe the RNA-Induced Transcriptional Silencing (RITS) RNAi complex mediates heterochromatin formation at non-coding and repetitive DNA. However, the targeting and role of RITS at other genomic regions, including protein-coding genes, remain unknown. Here we show that RITS localizes to specific meiotic genes and mRNAs. Remarkably, RITS is guided to these meiotic targets by the RNA-binding protein Mmi1 and its associated RNA surveillance machinery that together degrade selective meiotic mRNAs during vegetative growth. Upon sexual differentiation, RITS localization to the meiotic genes and mRNAs is lost. Large-scale identification of Mmi1 RNA targets reveals that RITS subunit Chp1 associates with the vast majority of them. In addition, loss of RNAi affects the effective repression of sexual differentiation mediated by the Mmi1 RNA surveillance machinery. These findings uncover a new mechanism for recruiting RNAi to specific meiotic genes and suggest that RNAi participates in the control of sexual differentiation in fission yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
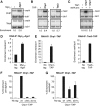
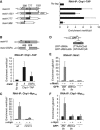
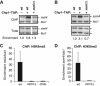
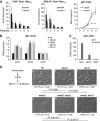
Comment in
-
New romance between RNA degradation pathways: Mmi1 and RNAi meet on heterochromatic islands.EMBO J. 2012 May 16;31(10):2242-3. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.138. Epub 2012 May 1. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22549465 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
New romance between RNA degradation pathways: Mmi1 and RNAi meet on heterochromatic islands.EMBO J. 2012 May 16;31(10):2242-3. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.138. Epub 2012 May 1. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22549465 Free PMC article.
-
YTH-RNA-binding protein prevents deleterious expression of meiotic proteins by tethering their mRNAs to nuclear foci.Elife. 2018 Feb 9;7:e32155. doi: 10.7554/eLife.32155. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29424342 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference (RNAi)-dependent and RNAi-independent association of the Chp1 chromodomain protein with distinct heterochromatic loci in fission yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Mar;25(6):2331-46. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.6.2331-2346.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15743828 Free PMC article.
-
RITS-connecting transcription, RNA interference, and heterochromatin assembly in fission yeast.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Sep-Oct;2(5):632-46. doi: 10.1002/wrna.80. Epub 2011 Mar 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21823226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies on the mechanism of RNAi-dependent heterochromatin assembly.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:461-71. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.044. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381328 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-Mediated Regulation of Meiosis in Budding Yeast.Noncoding RNA. 2022 Nov 15;8(6):77. doi: 10.3390/ncrna8060077. Noncoding RNA. 2022. PMID: 36412912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distribution, Characteristics, and Regulatory Potential of Long Noncoding RNAs in Brown-Rot Fungi.Int J Genomics. 2019 May 2;2019:9702342. doi: 10.1155/2019/9702342. eCollection 2019. Int J Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31192251 Free PMC article.
-
MhYTP1 and MhYTP2 from Apple Confer Tolerance to Multiple Abiotic Stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Aug 4;8:1367. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01367. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28824695 Free PMC article.
-
Dependency of Heterochromatin Domains on Replication Factors.G3 (Bethesda). 2018 Feb 2;8(2):477-489. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.300341. G3 (Bethesda). 2018. PMID: 29187422 Free PMC article.
-
Hexanucleotide motifs mediate recruitment of the RNA elimination machinery to silent meiotic genes.Open Biol. 2012 Mar;2(3):120014. doi: 10.1098/rsob.120014. Open Biol. 2012. PMID: 22645662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bahler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, Shah NG, McKenzie A 3rd, Steever AB, Wach A, Philippsen P, Pringle JR (1998) Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 14: 943–951 - PubMed
-
- Bourc'his D, Voinnet O (2010) A small-RNA perspective on gametogenesis, fertilization, and early zygotic development. Science 330: 6004617–622 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

