Rare and common variants in CARD14, encoding an epidermal regulator of NF-kappaB, in psoriasis
- PMID: 22521419
- PMCID: PMC3376540
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.03.013
Rare and common variants in CARD14, encoding an epidermal regulator of NF-kappaB, in psoriasis
Abstract
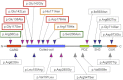
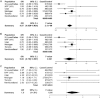
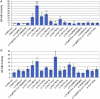
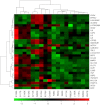
Psoriasis is a common inflammatory disorder of the skin and other organs. We have determined that mutations in CARD14, encoding a nuclear factor of kappa light chain enhancer in B cells (NF-kB) activator within skin epidermis, account for PSORS2. Here, we describe fifteen additional rare missense variants in CARD14, their distribution in seven psoriasis cohorts (>6,000 cases and >4,000 controls), and their effects on NF-kB activation and the transcriptome of keratinocytes. There were more CARD14 rare variants in cases than in controls (burden test p value = 0.0015). Some variants were only seen in a single case, and these included putative pathogenic mutations (c.424G>A [p.Glu142Lys] and c.425A>G [p.Glu142Gly]) and the generalized-pustular-psoriasis mutation, c.413A>C (p.Glu138Ala); these three mutations lie within the coiled-coil domain of CARD14. The c.349G>A (p.Gly117Ser) familial-psoriasis mutation was present at a frequency of 0.0005 in cases of European ancestry. CARD14 variants led to a range of NF-kB activities; in particular, putative pathogenic variants led to levels >2.5× higher than did wild-type CARD14. Two variants (c.511C>A [p.His171Asn] and c.536G>A [p.Arg179His]) required stimulation with tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) to achieve significant increases in NF-kB levels. Transcriptome profiling of wild-type and variant CARD14 transfectants in keratinocytes differentiated probably pathogenic mutations from neutral variants such as polymorphisms. Over 20 CARD14 polymorphisms were also genotyped, and meta-analysis revealed an association between psoriasis and rs11652075 (c.2458C>T [p.Arg820Trp]; p value = 2.1 × 10(-6)). In the two largest psoriasis cohorts, evidence for association increased when rs11652075 was conditioned on HLA-Cw*0602 (PSORS1). These studies contribute to our understanding of the genetic basis of psoriasis and illustrate the challenges faced in identifying pathogenic variants in common disease.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical and Genetic Heterogeneity of CARD14 Mutations in Psoriatic Skin Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 16;9:2239. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02239. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30386326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PSORS2 is due to mutations in CARD14.Am J Hum Genet. 2012 May 4;90(5):784-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.03.012. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22521418 Free PMC article.
-
CARD14 alterations in Tunisian patients with psoriasis and further characterization in European cohorts.Br J Dermatol. 2016 Feb;174(2):330-7. doi: 10.1111/bjd.14158. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Br J Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 26358359 Free PMC article.
-
The common CARD14 gene missense polymorphism rs11652075 (c.C2458T/p.Arg820Trp) is associated with psoriasis: a meta-analysis.Genet Mol Res. 2016 Aug 19;15(3). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15038357. Genet Mol Res. 2016. PMID: 27706581
-
CARD14-Mediated Activation of Paracaspase MALT1 in Keratinocytes: Implications for Psoriasis.J Invest Dermatol. 2017 Mar;137(3):569-575. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.09.031. Epub 2016 Dec 8. J Invest Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 27939769 Review.
Cited by
-
RAC1 activation drives pathologic interactions between the epidermis and immune cells.J Clin Invest. 2016 Jul 1;126(7):2661-77. doi: 10.1172/JCI85738. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27294528 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Genetic Heterogeneity of CARD14 Mutations in Psoriatic Skin Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 16;9:2239. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02239. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30386326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicastrin haploinsufficiency alters expression of type I interferon-stimulated genes: the relationship to familial hidradenitis suppurativa.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019 Jun;44(4):e118-e125. doi: 10.1111/ced.13906. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30656721 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of hyperthyroidism based on electronic medical record from Taiwan.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 27;9:830621. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.830621. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35991636 Free PMC article.
-
CARD14 Signalling Ensures Cell Survival and Cancer Associated Gene Expression in Prostate Cancer Cells.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 18;10(8):2008. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10082008. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lowes M.A., Bowcock A.M., Krueger J.G. Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature. 2007;445:866–873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AR050266/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007279/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR054966/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32AR007279/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000045/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HG000045/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL083822/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5RC1AR058681/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042742/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL083822/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM07200/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- R01 AR054966/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR050511/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007200/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR060222/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR060222/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AR057763/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058681/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08AR057763/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD052973/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- AR050266/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

