Protein kinase G inhibits flow-induced Ca2+ entry into collecting duct cells
- PMID: 22518003
- PMCID: PMC3380646
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2011100972
Protein kinase G inhibits flow-induced Ca2+ entry into collecting duct cells
Abstract
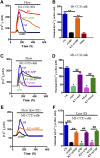
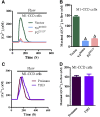
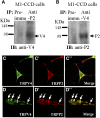
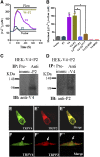
The renal cortical collecting duct (CCD) contributes to the maintenance of K(+) homeostasis by modulating renal K(+) secretion. Cytosolic Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)](i)) mediates flow-induced K(+) secretion in the CCD, but the mechanisms regulating flow-induced Ca(2+) entry into renal epithelial cells are not well understood. Here, we found that atrial natriuretic peptide, nitric oxide, and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) act through protein kinase G (PKG) to inhibit flow-induced increases in [Ca(2+)](i) in M1-CCD cells. Coimmunoprecipitation, double immunostaining, and functional studies identified heteromeric TRPV4-P2 channels as the mediators of flow-induced Ca(2+) entry into M1-CCD cells and HEK293 cells that were coexpressed with both TRPV4 and TRPP2. In these HEK293 cells, introducing point mutations at two putative PKG phosphorylation sites on TRPP2 abolished the ability of cGMP to inhibit flow-induced Ca(2+) entry. In addition, treating M1-CCD cells with fusion peptides that compete with the endogenous PKG phosphorylation sites on TRPP2 also abolished the cGMP-mediated inhibition of the flow-induced Ca(2+) entry. Taken together, these data suggest that heteromeric TRPV4-P2 channels mediate the flow-induced entry of Ca(2+) into collecting duct cells. Furthermore, substances such as atrial natriuretic peptide and nitric oxide, which increase cGMP, abrogate flow-induced Ca(2+) entry through PKG-mediated inhibition of these channels.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TRPP2 and TRPV4 form an EGF-activated calcium permeable channel at the apical membrane of renal collecting duct cells.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 16;8(8):e73424. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073424. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23977387 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic coupling between TRPV4 and Ca2+-activated SK1/3 and IK1 K+ channels plays a critical role in regulating the K+-secretory BK channel in kidney collecting duct cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):F1081-F1089. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00037.2017. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28274924 Free PMC article.
-
Uroguanylin and guanylin regulate transport of mouse cortical collecting duct independent of guanylate cyclase C.Kidney Int. 2005 Sep;68(3):1008-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00518.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 16105031
-
TRPC, cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cytosolic Ca2+.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007;(179):527-40. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34891-7_31. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17217077 Review.
-
Cyclic GMP and protein kinase-G in myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion: opportunities and obstacles for survival signaling.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Nov;152(6):855-69. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707409. Epub 2007 Aug 13. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17700722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Calcium channels in primary cilia.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016 Sep;25(5):452-8. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000251. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 27341444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
With-No-Lysine Kinase 1 (WNK1) Augments TRPV4 Function in the Aldosterone-Sensitive Distal Nephron.Cells. 2021 Jun 12;10(6):1482. doi: 10.3390/cells10061482. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34204757 Free PMC article.
-
A network perspective on unraveling the role of TRP channels in biology and disease.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Feb;466(2):173-82. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1292-2. Epub 2013 May 16. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 23677537 Review.
-
Exocyst controls exosome biogenesis via Rab11a.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Dec 17;27:535-546. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.12.023. eCollection 2022 Mar 8. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 35036064 Free PMC article.
-
A novel antagonist of TRPM2 and TRPV4 channels: Carvacrol.Metab Brain Dis. 2022 Mar;37(3):711-728. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00887-1. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Metab Brain Dis. 2022. PMID: 34989943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giebisch G: Renal potassium transport: Mechanisms and regulation. Am J Physiol 274: F817–F833, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Liu W, Morimoto T, Woda C, Kleyman TR, Satlin LM: Ca2+ dependence of flow-stimulated K secretion in the mammalian cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 293: F227–F235, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Satlin LM, Sheng S, Woda CB, Kleyman TR: Epithelial Na(+) channels are regulated by flow. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280: F1010–F1018, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Zeidel ML: Renal actions of atrial natriuretic peptide: Regulation of collecting duct sodium and water transport. Annu Rev Physiol 52: 747–759, 1990 - PubMed
-
- Ortiz PA, Garvin JL: Role of nitric oxide in the regulation of nephron transport. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282: F777–F784, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

