Arcuate kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons mediate the estrogen suppression of gonadotropin secretion and body weight
- PMID: 22508514
- PMCID: PMC3359616
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2012-1045
Arcuate kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons mediate the estrogen suppression of gonadotropin secretion and body weight
Abstract
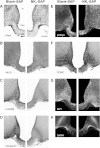
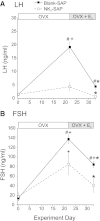
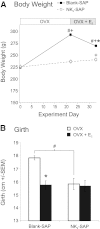
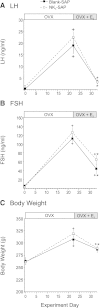
Estrogen withdrawal increases gonadotropin secretion and body weight, but the critical cell populations mediating these effects are not well understood. Recent studies have focused on a subpopulation of hypothalamic arcuate neurons that coexpress estrogen receptor α, neurokinin 3 receptor (NK(3)R), kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin for the regulation of reproduction. To investigate the function of kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons, a novel method was developed to ablate these cells using a selective NK(3)R agonist conjugated to the ribosome-inactivating toxin, saporin (NK(3)-SAP). Stereotaxic injections of NK(3)-SAP in the arcuate nucleus ablated KNDy neurons, as demonstrated by the near-complete loss of NK(3)R, NKB, and kisspeptin-immunoreactive (ir) neurons and depletion of the majority of arcuate dynorphin-ir neurons. Selectivity was demonstrated by the preservation of proopiomelanocortin, neuropeptide Y, and GnRH-ir elements in the arcuate nucleus and median eminence. In control rats, ovariectomy (OVX) markedly increased serum LH, FSH, and body weight, and these parameters were subsequently decreased by treatment with 17β-estradiol. KNDy neuron ablation prevented the rise in serum LH after OVX and attenuated the rise in serum FSH. KNDy neuron ablation did not completely block the suppressive effects of E(2) on gonadotropin secretion, a finding consistent with redundant pathways for estrogen negative feedback. However, regardless of estrogen status, KNDy-ablated rats had lower levels of serum gonadotropins compared with controls. Surprisingly, KNDy neuron ablation prevented the dramatic effects of OVX and 17β-estradiol (E(2)) replacement on body weight and abdominal girth. These data provide evidence that arcuate KNDy neurons are essential for tonic gonadotropin secretion, the rise in LH after removal of E(2), and the E(2) modulation of body weight.
Figures

Similar articles
-
KNDy Neurons Modulate the Magnitude of the Steroid-Induced Luteinizing Hormone Surges in Ovariectomized Rats.Endocrinology. 2015 Nov;156(11):4200-13. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1070. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 26302111 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of KNDy Neurons Results in Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism and Amplifies the Steroid-Induced LH Surge in Female Rats.Endocrinology. 2016 May;157(5):2015-27. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1740. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Endocrinology. 2016. PMID: 26937713 Free PMC article.
-
The kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) cell population of the arcuate nucleus: sex differences and effects of prenatal testosterone in sheep.Endocrinology. 2010 Jan;151(1):301-11. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0541. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 19880810 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating the KNDy neuronal activities to generate and modulate GnRH pulse in mammals.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2022 Jan;64:100968. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2021.100968. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2022. PMID: 34808231 Review.
-
Neuroendocrine control of gonadotropin-releasing hormone: Pulsatile and surge modes of secretion.J Neuroendocrinol. 2022 May;34(5):e13094. doi: 10.1111/jne.13094. Epub 2022 Feb 2. J Neuroendocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35107859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A role for neurokinin B in pulsatile GnRH secretion in the ewe.Neuroendocrinology. 2014;99(1):18-32. doi: 10.1159/000355285. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Neuroendocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24008670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KNDy Neurons Modulate the Magnitude of the Steroid-Induced Luteinizing Hormone Surges in Ovariectomized Rats.Endocrinology. 2015 Nov;156(11):4200-13. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1070. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 26302111 Free PMC article.
-
Neurokinin 3 Receptor-Expressing Neurons in the Median Preoptic Nucleus Modulate Heat-Dissipation Effectors in the Female Rat.Endocrinology. 2015 Jul;156(7):2552-62. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1974. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25825817 Free PMC article.
-
Role for kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons in cutaneous vasodilatation and the estrogen modulation of body temperature.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Nov 27;109(48):19846-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211517109. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23150555 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic Stimulation of Arcuate Nucleus Kiss1 Neurons Reveals a Steroid-Dependent Glutamatergic Input to POMC and AgRP Neurons in Male Mice.Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Jun;30(6):630-44. doi: 10.1210/me.2016-1026. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27093227 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tarttelin MF, Gorski RA. 1973. The effects of ovarian steroids on food and water intake and body weight in the female rat. Acta Endocrinol 72:551–568 - PubMed
-
- Rance NE, McMullen NT, Smialek JE, Price DL, Young WS., 3rd 1990. Postmenopausal hypertrophy of neurons expressing the estrogen receptor gene in the human hypothalamus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 71:79–85 - PubMed
-
- Rance NE, Young WS., 3rd 1991. Hypertrophy and increased gene expression of neurons containing neurokinin-B and substance-P messenger ribonucleic acids in the hypothalami of postmenopausal women. Endocrinology 128:2239–2247 - PubMed
-
- Rometo AM, Krajewski SJ, Voytko ML, Rance NE. 2007. Hypertrophy and increased kisspeptin gene expression in the hypothalamic infundibular nucleus of postmenopausal women and ovariectomized monkeys. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:2744–2750 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

