Identification of common variants associated with human hippocampal and intracranial volumes
- PMID: 22504417
- PMCID: PMC3635491
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2250
Identification of common variants associated with human hippocampal and intracranial volumes
Abstract
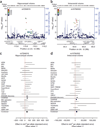
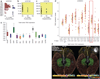
Identifying genetic variants influencing human brain structures may reveal new biological mechanisms underlying cognition and neuropsychiatric illness. The volume of the hippocampus is a biomarker of incipient Alzheimer's disease and is reduced in schizophrenia, major depression and mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Whereas many brain imaging phenotypes are highly heritable, identifying and replicating genetic influences has been difficult, as small effects and the high costs of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have led to underpowered studies. Here we report genome-wide association meta-analyses and replication for mean bilateral hippocampal, total brain and intracranial volumes from a large multinational consortium. The intergenic variant rs7294919 was associated with hippocampal volume (12q24.22; N = 21,151; P = 6.70 × 10(-16)) and the expression levels of the positional candidate gene TESC in brain tissue. Additionally, rs10784502, located within HMGA2, was associated with intracranial volume (12q14.3; N = 15,782; P = 1.12 × 10(-12)). We also identified a suggestive association with total brain volume at rs10494373 within DDR2 (1q23.3; N = 6,500; P = 5.81 × 10(-7)).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Common variants at 12q14 and 12q24 are associated with hippocampal volume.Nat Genet. 2012 Apr 15;44(5):545-51. doi: 10.1038/ng.2237. Nat Genet. 2012. PMID: 22504421 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal imaging of a tescalcin (TESC)-regulating polymorphism (rs7294919)-specific effects on hippocampal gray matter structure.Mol Psychiatry. 2015 Mar;20(3):398-404. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.39. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Mol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 24776739
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism rs7294919 on chromosome 12q24.22 is associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease in Han Chinese.Neurosci Lett. 2014 Feb 7;560:67-70. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.12.022. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Neurosci Lett. 2014. PMID: 24361131
-
Imaging genetics and psychiatric disorders.Curr Mol Med. 2015;15(2):168-75. doi: 10.2174/1566524015666150303104159. Curr Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25732148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ENIGMA Consortium: large-scale collaborative analyses of neuroimaging and genetic data.Brain Imaging Behav. 2014 Jun;8(2):153-82. doi: 10.1007/s11682-013-9269-5. Brain Imaging Behav. 2014. PMID: 24399358 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An association between human hippocampal volume and topographical memory in healthy young adults.Front Hum Neurosci. 2012 Dec 31;6:338. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2012.00338. eCollection 2012. Front Hum Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23293595 Free PMC article.
-
APOE and BCHE as modulators of cerebral amyloid deposition: a florbetapir PET genome-wide association study.Mol Psychiatry. 2014 Mar;19(3):351-7. doi: 10.1038/mp.2013.19. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Mol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 23419831 Free PMC article.
-
A commonly carried genetic variant in the delta opioid receptor gene, OPRD1, is associated with smaller regional brain volumes: replication in elderly and young populations.Hum Brain Mapp. 2014 Apr;35(4):1226-36. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22247. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014. PMID: 23427138 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Brain Imaging Reveals Structural Differences in Alzheimer's Disease Polygenic Risk Carriers: A Study in Healthy Young Adults.Biol Psychiatry. 2017 Jan 15;81(2):154-161. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.02.033. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Biol Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 27157680 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying genes associated with brain volumetric differences through tissue specific transcriptomic inference from GWAS summary data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Sep 28;23(Suppl 3):398. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04947-w. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 36171548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simić G, Kostovic I, Winblad B, Bogdanovic N. Volume and number of neurons of the human hippocampal formation in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997;379:482–494. - PubMed
-
- Wright IC, et al. Meta-analysis of regional brain volumes in schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2000;157:16–25. - PubMed
-
- Videbech P, Ravnkilde B. Hippocampal volume and depression: a meta-analysis of MRI studies. Am. J. Psychiatry. 2004;161:1957–1966. - PubMed
-
- Keller SS, Roberts N. Voxel-based morphometry of temporal lobe epilepsy: an introduction and review of the literature. Epilepsia. 2008;49:741–757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG040770/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH078075/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR017515/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- MH59490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH078111/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000117/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- G0901254/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K01 AG030514/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- SCD/10/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- ZIA MH002810/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG019771/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K01417X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1001401/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F019394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- U24 RR21992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0802462/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 EB015611/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG040060/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG010483/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0901858/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- T32 NS048004/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- HD050735/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- S10 RR029392/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG013846/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 EB006395/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- AG16570/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH079799/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH083824/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0700704/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ZIA MH002790/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH078111/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036535/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH078075/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 93558/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U24AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR13556/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- EB008432/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH087061/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR013556/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G1001245/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 AG016570/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036535-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD050735/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB008432/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 072894/z/03/z-Gill/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- ZIA MH002810-10/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- G0900908/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH079799/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01D0042157-01A/PHS HHS/United States
- K99 MH085098/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR013642/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U24 MH068457/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 084730/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AG019771-09/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 RR021992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- EB008281/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0600429/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R37 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U24 MH068457-06/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083824/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB008281/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- EB006395/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001998/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- AG040060/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MH0708143/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 8200/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- AG036535/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

