Dynamic transformations of genome-wide epigenetic marking and transcriptional control establish T cell identity
- PMID: 22500808
- PMCID: PMC3336965
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.056
Dynamic transformations of genome-wide epigenetic marking and transcriptional control establish T cell identity
Abstract
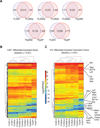
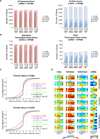
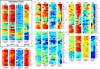
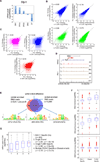
T cell development comprises a stepwise process of commitment from a multipotent precursor. To define molecular mechanisms controlling this progression, we probed five stages spanning the commitment process using RNA-seq and ChIP-seq to track genome-wide shifts in transcription, cohorts of active transcription factor genes, histone modifications at diverse classes of cis-regulatory elements, and binding repertoire of GATA-3 and PU.1, transcription factors with complementary roles in T cell development. The results highlight potential promoter-distal cis-regulatory elements in play and reveal both activation sites and diverse mechanisms of repression that silence genes used in alternative lineages. Histone marking is dynamic and reversible, and though permissive marks anticipate, repressive marks often lag behind changes in transcription. In vivo binding of PU.1 and GATA-3 relative to epigenetic marking reveals distinctive factor-specific rules for recruitment of these crucial transcription factors to different subsets of their potential sites, dependent on dose and developmental context.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Architecture of a lymphomyeloid developmental switch controlled by PU.1, Notch and Gata3.Development. 2013 Mar;140(6):1207-19. doi: 10.1242/dev.088559. Development. 2013. PMID: 23444353 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of early T-lineage gene expression and developmental progression by the progenitor cell transcription factor PU.1.Genes Dev. 2015 Apr 15;29(8):832-48. doi: 10.1101/gad.259879.115. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Genes Dev. 2015. PMID: 25846797 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation of PU.1 With IRF8 and NFATc1 Defines Chromatin Landscapes During RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis.J Bone Miner Res. 2019 Jun;34(6):1143-1154. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3689. Epub 2019 Feb 28. J Bone Miner Res. 2019. PMID: 30721543
-
Transcriptional establishment of cell-type identity: dynamics and causal mechanisms of T-cell lineage commitment.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2013;78:31-41. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2013.78.020271. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2013. PMID: 24135716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Forging T-Lymphocyte Identity: Intersecting Networks of Transcriptional Control.Adv Immunol. 2016;129:109-74. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2015.09.002. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Adv Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26791859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Erg-driven transcriptional program controls B cell lymphopoiesis.Nat Commun. 2020 Jun 15;11(1):3013. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16828-y. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32541654 Free PMC article.
-
ChromTime: modeling spatio-temporal dynamics of chromatin marks.Genome Biol. 2018 Aug 10;19(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1485-2. Genome Biol. 2018. PMID: 30097049 Free PMC article.
-
Misregulation of the IgH Locus in Thymocytes.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 13;9:2426. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02426. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30483245 Free PMC article.
-
T-ALL leukemia stem cell 'stemness' is epigenetically controlled by the master regulator SPI1.Elife. 2018 Nov 9;7:e38314. doi: 10.7554/eLife.38314. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30412053 Free PMC article.
-
3D Genome Organization as an Epigenetic Determinant of Transcription Regulation in T Cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 22;13:921375. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.921375. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35812421 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
-
- Decker T, Pasca dM, McManus S, Sun Q, Bonifer C, Tagoh H, Busslinger M. Stepwise activation of enhancer and promoter regions of the B cell commitment gene Pax5 in early lymphopoiesis. Immunity. 2009;30:508–520. - PubMed
-
- DeKoter RP, Lee H-J, Singh H. PU.1 regulates expression of the Interleukin-7 receptor in lymphoid progenitors. Immunity. 2002;16:297–309. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson IJ, Chapman M, Kinston S, Landry JR, Knezevic K, Piltz S, Buckley N, Green AR, Gottgens B. Genome-wide identification of cis-regulatory sequences controlling blood and endothelial development. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005;14:595–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R33 HL089123/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2CA148278/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI095943/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148278/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA090233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148278-02/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA090233-10/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA090233-08S1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA090233-08S1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA090233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 HL089123-03/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R33HL089123/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

