Intimal lining layer macrophages but not synovial sublining macrophages display an IL-10 polarized-like phenotype in chronic synovitis
- PMID: 22494514
- PMCID: PMC3446447
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3796
Intimal lining layer macrophages but not synovial sublining macrophages display an IL-10 polarized-like phenotype in chronic synovitis
Abstract
Introduction: Synovial tissue macrophages play a key role in chronic inflammatory arthritis, but the contribution of different macrophage subsets in this process remains largely unknown. The main in vitro polarized macrophage subsets are classically (M1) and alternatively (M2) activated macrophages, the latter comprising interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-10 polarized cells. Here, we aimed to evaluate the polarization status of synovial macrophages in spondyloarthritis (SpA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
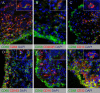
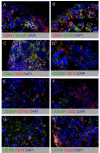
Methods: Expression of polarization markers on synovial macrophages, peripheral blood monocytes, and in vitro polarized monocyte-derived macrophages from SpA versus RA patients was assessed by immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry, respectively. The polarization status of the intimal lining layer and the synovial sublining macrophages was assessed by double immunofluorescence staining.
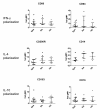
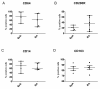
Results: The expression of the IL-10 polarization marker cluster of differentiation 163 (CD163) was increased in SpA compared with RA intimal lining layer, but no differences were found in other M1 and M2 markers between the diseases. Furthermore, no significant phenotypic differences in monocytes and in vitro polarized monocyte-derived macrophages were seen between SpA, RA, and healthy controls, indicating that the differential CD163 expression does not reflect a preferential M2 polarization in SpA. More detailed analysis of intimal lining layer macrophages revealed a strong co-expression of the IL-10 polarization markers CD163 and cluster of differentiation 32 (CD32) but not any of the other markers in both SpA and RA. In contrast, synovial sublining macrophages had a more heterogeneous phenotype, with a majority of cells co-expressing M1 and M2 markers.
Conclusions: The intimal lining layer but not synovial sublining macrophages display an IL-10 polarized-like phenotype, with increased CD163 expression in SpA versus RA synovitis. These differences in the distribution of the polarized macrophage subset may contribute to the outcome of chronic synovitis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Infiltration of the synovial membrane with macrophage subsets and polymorphonuclear cells reflects global disease activity in spondyloarthropathy.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(2):R359-69. doi: 10.1186/ar1501. Epub 2005 Jan 21. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15743484 Free PMC article.
-
GM-CSF Expression and Macrophage Polarization in Joints of Undifferentiated Arthritis Patients Evolving to Rheumatoid Arthritis or Psoriatic Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 17;11:613975. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.613975. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679701 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of a classically activated macrophage cytokine signature in peripheral spondylarthritis, including psoriatic arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Apr;60(4):966-75. doi: 10.1002/art.24406. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19333931
-
The Role of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovitis.Front Immunol. 2022 May 19;13:867260. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.867260. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35663975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage polarization in rheumatoid arthritis: signaling pathways, metabolic reprogramming, and crosstalk with synovial fibroblasts.Front Immunol. 2024 May 10;15:1394108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1394108. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38799455 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Poly-dopamine, poly-levodopa, and poly-norepinephrine coatings: Comparison of physico-chemical and biological properties with focus on the application for blood-contacting devices.Bioact Mater. 2020 Aug 24;6(1):285-296. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.06.024. eCollection 2021 Jan. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 32913935 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the gut-joint axis: links between gut inflammation and spondyloarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Aug;16(8):415-433. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0454-9. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32661321 Review.
-
Macrophage Activities in Myocardial Infarction and Heart Failure.Cardiol Res Pract. 2020 Apr 22;2020:4375127. doi: 10.1155/2020/4375127. eCollection 2020. Cardiol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32377427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation Effects of Toxoplasma gondii Histone H2A1 on Murine Macrophages and Encapsulation with Polymer as a Vaccine Candidate.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Dec 3;8(4):731. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8040731. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33287313 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcoidosis and Cancer: The Role of the Granulomatous Reaction as a Double-Edged Sword.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 4;13(17):5232. doi: 10.3390/jcm13175232. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274446 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

