Synaptic activity unmasks dopamine D2 receptor modulation of a specific class of layer V pyramidal neurons in prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 22492051
- PMCID: PMC3352768
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5835-11.2012
Synaptic activity unmasks dopamine D2 receptor modulation of a specific class of layer V pyramidal neurons in prefrontal cortex
Abstract
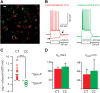
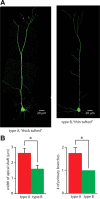
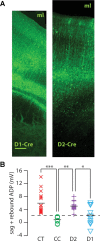
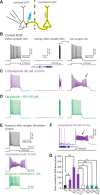
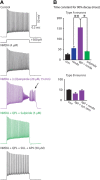
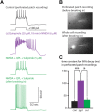
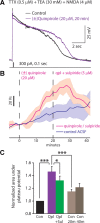
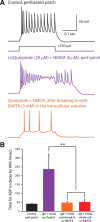
Dopamine D2 receptors (D2Rs) play a major role in the function of the prefrontal cortex (PFC), and may contribute to prefrontal dysfunction in conditions such as schizophrenia. Here we report that in mouse PFC, D2Rs are selectively expressed by a subtype of layer V pyramidal neurons that have thick apical tufts, prominent h-current, and subcortical projections. Within this subpopulation, the D2R agonist quinpirole elicits a novel afterdepolarization that generates voltage fluctuations and spiking for hundreds of milliseconds. Surprisingly, this afterdepolarization is masked in quiescent brain slices, but is readily unmasked by physiologic levels of synaptic input which activate NMDA receptors, possibly explaining why this phenomenon has not been reported previously. Notably, we could still elicit this afterdepolarization for some time after the cessation of synaptic stimulation. In addition to NMDA receptors, the quinpirole-induced afterdepolarization also depended on L-type Ca(2+) channels and was blocked by the selective L-type antagonist nimodipine. To confirm that D2Rs can elicit this afterdepolarization by enhancing Ca(2+) (and Ca(2+)-dependent) currents, we measured whole-cell Ca(2+) potentials that occur after blocking Na(+) and K(+) channels, and found quinpirole enhanced these potentials, while the selective D2R antagonist sulpiride had the opposite effect. Thus, D2Rs can elicit a Ca(2+)-channel-dependent afterdepolarization that powerfully modulates activity in specific prefrontal neurons. Through this mechanism, D2Rs might enhance outputs to subcortical structures, contribute to reward-related persistent firing, or increase the level of noise in prefrontal circuits.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dopamine D2 Receptors Modulate Pyramidal Neurons in Mouse Medial Prefrontal Cortex through a Stimulatory G-Protein Pathway.J Neurosci. 2017 Oct 18;37(42):10063-10073. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1893-17.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 14. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28912160 Free PMC article.
-
Subtype-specific effects of dopaminergic D2 receptor activation on synaptic trains in layer V pyramidal neurons in the mouse prefrontal cortex.Physiol Rep. 2017 Nov;5(22):e13499. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13499. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29150590 Free PMC article.
-
D2 dopamine receptors recruit a GABA component for their attenuation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the adult rat prefrontal cortex.Synapse. 2007 Oct;61(10):843-50. doi: 10.1002/syn.20432. Synapse. 2007. PMID: 17603809 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a neuronal model for the pathophysiology of schizophrenia based on the nature of electrophysiological actions of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex.Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999 Aug;21(2):161-94. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00112-2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999. PMID: 10432466 Review.
-
The prefrontal cortex: a target for antipsychotic drugs.Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2010 Jan;121(1):11-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.2009.01455.x. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2010. PMID: 20059453 Review.
Cited by
-
Adolescent maturation of inhibitory inputs onto cingulate cortex neurons is cell-type specific and TrkB dependent.Front Neural Circuits. 2015 Feb 16;9:5. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2015.00005. eCollection 2015. Front Neural Circuits. 2015. PMID: 25762898 Free PMC article.
-
We're not in Kansas anymore: ectopic dopaminergic terminals as an explanation for the positive symptoms in psychiatric pathology.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2023 Feb 21;48(1):E74-E77. doi: 10.1503/jpn.230015. Print 2023 Jan-Feb. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36810305 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Concussive Head Trauma Deranges Axon Initial Segment Function in Axotomized and Intact Layer 5 Pyramidal Neurons.J Neurotrauma. 2024 Jan;41(1-2):244-270. doi: 10.1089/neu.2022.0469. Epub 2023 Oct 17. J Neurotrauma. 2024. PMID: 37650832 Free PMC article.
-
Prefrontal cortex circuits in depression and anxiety: contribution of discrete neuronal populations and target regions.Mol Psychiatry. 2020 Nov;25(11):2742-2758. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-0685-9. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Mol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32086434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasticity in Prefrontal Cortex Induced by Coordinated Synaptic Transmission Arising from Reuniens/Rhomboid Nuclei and Hippocampus.Cereb Cortex Commun. 2021 Apr 14;2(2):tgab029. doi: 10.1093/texcom/tgab029. eCollection 2021. Cereb Cortex Commun. 2021. PMID: 34296174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn S, Shenoy SK, Wei H, Lefkowitz RJ. Differential kinetic and spatial patterns of beta-arrestin and G protein-mediated ERK activation by the angiotensin II receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:35518–35525. - PubMed
-
- Arnsten AF, Goldman-Rakic PS. Noise stress impairs prefrontal cortical cognitive function in monkeys: evidence for a hyperdopaminergic mechanism. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55:362–368. - PubMed
-
- Bernardi G, Cherubini E, Marciani MG, Mercuri N, Stanzione P. Responses of intracellularly recorded cortical neurons to the iontophoretic application of dopamine. Brain Res. 1982;245:267–274. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
