Impaired clearance and enhanced pulmonary inflammatory/fibrotic response to carbon nanotubes in myeloperoxidase-deficient mice
- PMID: 22479306
- PMCID: PMC3316527
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030923
Impaired clearance and enhanced pulmonary inflammatory/fibrotic response to carbon nanotubes in myeloperoxidase-deficient mice
Abstract
Advancement of biomedical applications of carbonaceous nanomaterials is hampered by their biopersistence and pro-inflammatory action in vivo. Here, we used myeloperoxidase knockout B6.129X1-MPO (MPO k/o) mice and showed that oxidation and clearance of single walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) from the lungs of these animals after pharyngeal aspiration was markedly less effective whereas the inflammatory response was more robust than in wild-type C57Bl/6 mice. Our results provide direct evidence for the participation of MPO - one of the key-orchestrators of inflammatory response - in the in vivo pulmonary oxidative biodegradation of SWCNT and suggest new ways to control the biopersistence of nanomaterials through genetic or pharmacological manipulations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
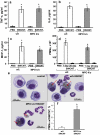
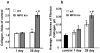
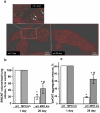
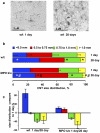
Similar articles
-
Pulmonary exposure to single-walled carbon nanotubes does not affect the early immune response against Toxoplasma gondii.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2012 May 23;9:16. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-9-16. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22621311 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative proteomics and pulmonary toxicity of instilled single-walled carbon nanotubes, crocidolite asbestos, and ultrafine carbon black in mice.Toxicol Sci. 2011 Mar;120(1):123-35. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq363. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Toxicol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21135415 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term effects of carbon containing engineered nanomaterials and asbestos in the lung: one year postexposure comparisons.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Jan;306(2):L170-82. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00167.2013. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24213921 Free PMC article.
-
A review of toxicity studies of single-walled carbon nanotubes in laboratory animals.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016 Feb;74:42-63. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2015.11.015. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26619783 Review.
-
Enzymatic oxidative biodegradation of nanoparticles: Mechanisms, significance and applications.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 May 15;299:58-69. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26768553 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of metal oxide nanoparticles in histopathological changes observed in the lung of welders.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014 May 13;11:23. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-11-23. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24885771 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of fiber length on carbon nanotube-induced fibrogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 29;15(5):7444-61. doi: 10.3390/ijms15057444. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24786100 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of cancer-associated fibroblast-like cells by carbon nanotubes dictates its tumorigenicity.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 20;6:39558. doi: 10.1038/srep39558. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27996035 Free PMC article.
-
A natural vanishing act: the enzyme-catalyzed degradation of carbon nanomaterials.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Oct 16;45(10):1770-81. doi: 10.1021/ar300106h. Epub 2012 Jul 23. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22824066 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotoxicity of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials, Starring Phagocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 10;23(16):8889. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168889. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012161 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muller J, Huaux F, Moreau N, Misson P, Heilier JF, et al. Respiratory toxicity of multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005;207:221–231. - PubMed
-
- Shvedova AA, Kagan VE, Fadeel B. Close encounters of the small kind: adverse effects of man-made materials interfacing with the nano-cosmos of biological systems. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2010;50:63–88. - PubMed
-
- Shvedova AA, Kisin ER, Mercer R, Murray AR, Johnson VJ, et al. Unusual inflammatory and fibrogenic pulmonary responses to single-walled carbon nanotubes in mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005;289:L698–708. - PubMed
-
- Park EJ, Roh J, Kim SN, Kang MS, Han YA, et al. A single intratracheal instillation of single-walled carbon nanotubes induced early lung fibrosis and subchronic tissue damage in mice. Arch Toxicol. 2011;85:1121–1131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL070755/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 OH008282/OH/NIOSH CDC HHS/United States
- U19 AI068021/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- LM007994-05/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- HL094488/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES019304/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI068021/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- OH008282/OH/NIOSH CDC HHS/United States
- HL70755/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES019304/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 LM007994/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM103529/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL094488/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

