The helicase and RNaseIIIa domains of Arabidopsis Dicer-Like1 modulate catalytic parameters during microRNA biogenesis
- PMID: 22474216
- PMCID: PMC3406889
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.112.193508
The helicase and RNaseIIIa domains of Arabidopsis Dicer-Like1 modulate catalytic parameters during microRNA biogenesis
Abstract
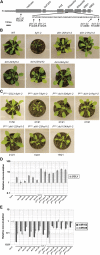
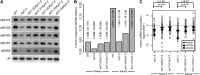
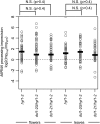
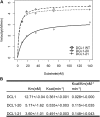
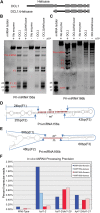
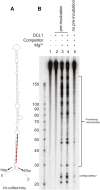
Dicer-Like1 (DCL1), an RNaseIII endonuclease, and Hyponastic Leaves1 (HYL1), a double-stranded RNA-binding protein, are core components of the plant microRNA (miRNA) biogenesis machinery. hyl1 null mutants accumulate low levels of miRNAs and display pleiotropic developmental phenotypes. We report the identification of five new hyl1 suppressor mutants, all of which are alleles of DCL1. These new alleles affect either the helicase or the RNaseIIIa domains of DCL1, highlighting the critical functions of these domains. Biochemical analysis of the DCL1 suppressor variants reveals that they process the primary transcript (pri-miRNA) more efficiently than wild-type DCL1, with both higher K(cat) and lower K(m) values. The DCL1 variants largely rescue wild-type miRNA accumulation levels in vivo, but do not rescue the MIRNA processing precision defects of the hyl1 null mutant. In vitro, the helicase domain confers ATP dependence on DCL1-catalyzed MIRNA processing, attenuates DCL1 cleavage activity, and is required for precise MIRNA processing of some substrates.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A dominant mutation in DCL1 suppresses the hyl1 mutant phenotype by promoting the processing of miRNA.RNA. 2009 Mar;15(3):450-8. doi: 10.1261/rna.1297109. Epub 2009 Jan 20. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19155326 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between DCL1 and HYL1 is important for efficient and precise processing of pri-miRNA in plant microRNA biogenesis.RNA. 2006 Feb;12(2):206-12. doi: 10.1261/rna.2146906. RNA. 2006. PMID: 16428603 Free PMC article.
-
Complementation of HYPONASTIC LEAVES1 by double-strand RNA-binding domains of DICER-LIKE1 in nuclear dicing bodies.Plant Physiol. 2013 Sep;163(1):108-17. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.219071. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23886622 Free PMC article.
-
Keeping up with the miRNAs: current paradigms of the biogenesis pathway.J Exp Bot. 2023 Apr 9;74(7):2213-2227. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac322. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 35959860 Review.
-
HYL1's multiverse: A journey through miRNA biogenesis and beyond canonical and non-canonical functions of HYL1.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024 Aug;80:102546. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2024.102546. Epub 2024 May 7. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38718678 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyponastic Leaves 1 protects pri-miRNAs from nuclear exosome attack.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 21;117(29):17429-17437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2007203117. Epub 2020 Jul 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32636270 Free PMC article.
-
Spliceosome disassembly factors ILP1 and NTR1 promote miRNA biogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Sep 5;47(15):7886-7900. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz526. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31216029 Free PMC article.
-
The SnRK2 kinases modulate miRNA accumulation in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2017 Apr 18;13(4):e1006753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006753. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28419088 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of miRNA abundance by RNA binding protein TOUGH in Arabidopsis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 31;109(31):12817-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204915109. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22802657 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA156 conditions auxin sensitivity to enable growth plasticity in response to environmental changes in Arabidopsis.Nat Commun. 2023 Mar 22;14(1):1449. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36774-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36949101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Carrington JC. (2005) microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 121: 207–221 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

