Impact of microRNA regulation on variation in human gene expression
- PMID: 22456605
- PMCID: PMC3396366
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.132514.111
Impact of microRNA regulation on variation in human gene expression
Abstract
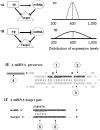
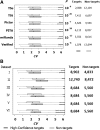
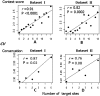
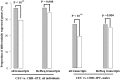
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenously expressed small RNAs that regulate expression of mRNAs at the post-transcriptional level. The consequence of miRNA regulation is hypothesized to reduce the expression variation of target genes. However, it is possible that mutations in miRNAs and target sites cause rewiring of the miRNA regulatory networks resulting in increased variation in gene expression. By examining variation in gene expression patterns in human populations and between human and other primate species, we find that miRNAs have stabilized expression of a small number of target genes during primate evolution. Compared with genes not regulated by miRNAs, however, genes regulated by miRNAs overall have higher expression variation at the population level, and they display greater variation in expression among human ethnic groups or between human and other primate species. By integrating expression data with genotypes determined in the HapMap 3 and the 1000 Genomes Projects, we found that expression variation in miRNAs, genetic variants in miRNA loci, and mutations in miRNA target sites are important sources of elevated expression variation of miRNA target genes. A reasonable case can be made that natural selection is driving this pattern of variation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Natural selection on human microRNA binding sites inferred from SNP data.Nat Genet. 2006 Dec;38(12):1452-6. doi: 10.1038/ng1910. Epub 2006 Oct 29. Nat Genet. 2006. PMID: 17072316
-
Discovery of microRNA regulatory networks by integrating multidimensional high-throughput data.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;774:251-66. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5590-1_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23377977
-
mi-IsoNet: systems-scale microRNA landscape reveals rampant isoform-mediated gain of target interaction diversity and signaling specificity.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Sep 2;22(5):bbab091. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab091. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33855356 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA sponges: soaking up miRNAs for regulation of gene expression.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014 May-Jun;5(3):317-33. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1213. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2014. PMID: 24375960 Review.
-
Convergent and divergent evolution of microRNA-mediated regulation in metazoans.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2024 Apr;99(2):525-545. doi: 10.1111/brv.13033. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2024. PMID: 37987240 Review.
Cited by
-
The superoxide dismutase 1 3'UTR maintains high expression of the SOD1 gene in cancer cells: The involvement of the RNA-binding protein AUF-1.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Aug;85:33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25908445 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting human genetic interactions from cancer genome evolution.PLoS One. 2015 May 1;10(5):e0125795. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125795. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25933428 Free PMC article.
-
Early microRNA indicators of PPARα pathway activation in the liver.Toxicol Rep. 2020 Jun 23;7:805-815. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2020.06.006. eCollection 2020. Toxicol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32642447 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for conserved post-transcriptional roles of unitary pseudogenes and for frequent bifunctionality of mRNAs.Genome Biol. 2012 Nov 15;13(11):R102. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-11-r102. Genome Biol. 2012. PMID: 23153069 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of miRNA Expression in Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Investigating Diagnostic Potential and Clinical Implications.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Feb 23;17:881-891. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S443755. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 38414865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Sung GH, Spatafora JW, Carrington JC 2004. Evolution of microRNA genes by inverted duplication of target gene sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 36: 1282–1290 - PubMed
-
- Ambros V 2003. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: Growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell 113: 673–676 - PubMed
-
- Bagga S, Bracht J, Hunter S, Massirer K, Holtz J, Eachus R, Pasquinelli AE 2005. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell 122: 553–563 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
