Chemokine receptor CXCR2: physiology regulator and neuroinflammation controller?
- PMID: 22445294
- PMCID: PMC3335977
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2012.02.016
Chemokine receptor CXCR2: physiology regulator and neuroinflammation controller?
Abstract
The innate immune system is a crucial component of inflammatory reactions, while the central nervous system (CNS) is the most vulnerable site of the body to inflammatory tissue injury. Neuroinflammatory brain pathologies are disorders in which the CNS is threatened by its own immune system. Chemokine receptor CXCR2 and its ligands have been implicated in several neuroinflammatory brain pathologies, as well as in neutrophil recruitment and in the developmental positioning of neural cells. This review focuses on the basics of CXCR2, its regulating role in bone marrow neutrophil recruitment, oligodendrocyte progenitor cell positioning and neural repair mechanisms, as well as its diverse roles in neuroinflammatory brain pathologies.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

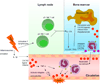
Injury activates γδ and natural killer T cells, which produces IL-17A. This induces transcription of G-CSF in the bone marrow, which activates TPO. Stimulation by TPO inhibits CXCL12-CXCR4 binding and activates the release of CXCR2 ligands from megakaryocytes. The release of the CXCR2 ligands and weakening of the CXCR2 binding, leads to mobilization of neutrophils from the bone marrow.
Activation of inflammasomes leads to IL-1β release and stimulation of local CXCR2 ligand production, inducing a subsequential production of TNF-α and LTB4, therewith activating integrins and selectins on the endothelial cells close the site of the lesion. CXCR2 ligands are presented at the site of the lesion, creating a chemotactic gradient for the recruitment of neutrophils through the interaction of CXCR2 and CXCR2 ligands.
Similar articles
-
Defective regulation of CXCR2 facilitates neutrophil release from bone marrow causing spontaneous inflammation in severely NF-kappa B-deficient mice.J Immunol. 2010 Jul 1;185(1):670-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000339. Epub 2010 Jun 2. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20519647 Free PMC article.
-
CXC chemokine receptor 2 but not C-C chemokine receptor 1 expression is essential for neutrophil recruitment to the cornea in helminth-mediated keratitis (river blindness).J Immunol. 2001 Mar 15;166(6):4035-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.6.4035. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11238651
-
Role of chemokines in CNS health and pathology: a focus on the CCL2/CCR2 and CXCL8/CXCR2 networks.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010 Mar;30(3):459-73. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2009.240. Epub 2009 Nov 11. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2010. PMID: 19904283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opposing effects mediated by the chemokine receptor CXCR2 on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: recruitment of potentially damaging neutrophils and direct myocardial protection.Circulation. 2003 Nov 11;108(19):2387-92. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000093192.72099.9A. Epub 2003 Oct 20. Circulation. 2003. PMID: 14568904
-
Blockade of CXCR2 signalling: a potential therapeutic target for preventing neutrophil-mediated inflammatory diseases.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014 May;239(5):509-18. doi: 10.1177/1535370213520110. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014. PMID: 24625439 Review.
Cited by
-
Areca Thirteen Pill Improves Depression in Rat by Modulation of the Chemokine/Chemokine Receptor Axis.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):4633-4647. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03855-1. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38110645
-
Early Trypanosoma cruzi infection reprograms human epithelial cells.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:439501. doi: 10.1155/2014/439501. Epub 2014 Apr 9. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24812617 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL5 signaling is a shared pathway of neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier injury contributing to white matter injury in the immature brain.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Jan 6;13:6. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0474-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 26738635 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic islet inflammation: an emerging role for chemokines.J Mol Endocrinol. 2017 Jul;59(1):R33-R46. doi: 10.1530/JME-17-0042. Epub 2017 Apr 18. J Mol Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28420714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCR2 Blockade Mitigates Neural Cell Injury Following Preclinical Chorioamnionitis.Front Physiol. 2019 Apr 2;10:324. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00324. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31001130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahuja SK, Murphy PM. The CXC chemokines growth-regulated oncogene (GRO) alpha, GRObeta, GROgamma, neutrophil-activating peptide-2, and epithelial cell-derived neutrophil-activating peptide-78 are potent agonists for the type B, but not the type A, human interleukin-8 receptor. J. Biol Chem. 1996;271:20545–20550. - PubMed
-
- Ahuja SK, Ozcelik T, Milatovitch A, Francke U, Murphy PM. Molecular evolution of the human interleukin-8 receptor gene cluster. Nat. Genet. 1992;2:31–36. - PubMed
-
- Allen SJ, Crown SE, Handel TM. Chemokine: receptor structure, interactions, and antagonism. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007;25:787–820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

