Absolute quantitation of isoforms of post-translationally modified proteins in transgenic organism
- PMID: 22442259
- PMCID: PMC3412961
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M111.016568
Absolute quantitation of isoforms of post-translationally modified proteins in transgenic organism
Abstract
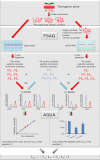
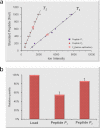
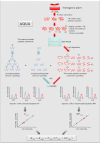
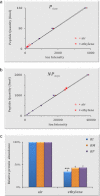
Post-translational modification isoforms of a protein are known to play versatile biological functions in diverse cellular processes. To measure the molar amount of each post-translational modification isoform (P(isf)) of a target protein present in the total protein extract using mass spectrometry, a quantitative proteomic protocol, absolute quantitation of isoforms of post-translationally modified proteins (AQUIP), was developed. A recombinant ERF110 gene overexpression transgenic Arabidopsis plant was used as the model organism for demonstration of the proof of concept. Both Ser-62-independent (14)N-coded synthetic peptide standards and (15)N-coded ERF110 protein standard isolated from the heavy nitrogen-labeled transgenic plants were employed simultaneously to determine the concentration of all isoforms (T(isf)) of ERF110 in the whole plant cell lysate, whereas a pair of Ser-62-dependent synthetic peptide standards were used to quantitate the Ser-62 phosphosite occupancy (R(aqu)). The P(isf) was finally determined by integrating the two empirically measured variables using the following equation: P(isf) = T(isf) · R(aqu). The absolute amount of Ser-62-phosphorylated isoform of ERF110 determined using AQUIP was substantiated with a stable isotope labeling in Arabidopsis-based relative and accurate quantitative proteomic approach. The biological role of the Ser-62-phosphorylated isoform was demonstrated in transgenic plants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Absolute quantitation of protein posttranslational modification isoform.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1306:105-19. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2648-0_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25930697
-
Functional phosphoproteomic analysis reveals that a serine-62-phosphorylated isoform of ethylene response factor110 is involved in Arabidopsis bolting.Plant Physiol. 2013 Feb;161(2):904-17. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.204487. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23188807 Free PMC article.
-
Stable isotope metabolic labeling-based quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of Arabidopsis mutants reveals ethylene-regulated time-dependent phosphoproteins and putative substrates of constitutive triple response 1 kinase.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013 Dec;12(12):3559-82. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M113.031633. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 24043427 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of Arabidopsis WRKY25 transcription factor in plant defense against Pseudomonas syringae.BMC Plant Biol. 2007 Jan 10;7:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-7-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2007. PMID: 17214894 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Phosphoproteomic Effects of Abscisic Acid (ABA) on Wild-Type and ABA Receptor-Deficient A. thaliana Mutants.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015 May;14(5):1169-82. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.043307. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25693798 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Quantitation, networking, and function of protein phosphorylation in plant cell.Front Plant Sci. 2013 Jan 8;3:302. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00302. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23316209 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of Dimethyl Labeling-based Quantitative Acetylproteomics in Arabidopsis.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018 May;17(5):1010-1027. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA117.000530. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29440448 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Pattern of ERF Gene Family under Multiple Abiotic Stresses in Populus simonii × P. nigra.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Feb 20;8:181. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00181. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28265277 Free PMC article.
-
Investment in plant research and development bears fruit in China.Plant Cell Rep. 2014 Apr;33(4):541-50. doi: 10.1007/s00299-014-1587-6. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Plant Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 24615161 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring of Plant Protein Post-translational Modifications Using Targeted Proteomics.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Aug 17;9:1168. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01168. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30174677 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mann M., Jensen O. N. (2003) Proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 255–261 - PubMed
-
- Witze E. S., Old W. M., Resing K. A., Ahn N. G. (2007) Mapping protein post-translational modifications with mass spectrometry. Nat. Methods 4, 798–806 - PubMed
-
- Krishna R. G., Wold F. (1993) Post-translational modification of proteins. Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas Mol. Biol. 67, 265–298 - PubMed
-
- Cohen P. (2002) The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat. Cell Biol. 4, E127–E130 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

