Galectin-9 binding to Tim-3 renders activated human CD4+ T cells less susceptible to HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 22438246
- PMCID: PMC3359739
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-11-389585
Galectin-9 binding to Tim-3 renders activated human CD4+ T cells less susceptible to HIV-1 infection
Abstract
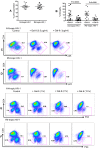
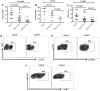
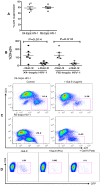
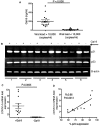
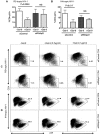
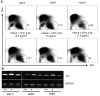
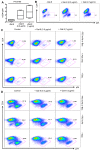
Galectin-9 (Gal-9) is a tandem repeat-type member of the galectin family and is a ligand for T-cell immunoglobulin mucin domain 3 (Tim-3), a type-I glycoprotein that is persistently expressed on dysfunctional T cells during chronic infection. Studies in autoimmune diseases and chronic viral infections show that Tim-3 is a regulatory molecule that inhibits Th1 type immune responses. Here we show that soluble Gal-9 interacts with Tim-3 expressed on the surface of activated CD4(+) T cells and renders them less susceptible to HIV-1 infection and replication. The Gal-9/Tim-3 interaction on activated CD4(+) T cells, leads to down-regulation of HIV-1 coreceptors and up-regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 (also known as cip-1 and waf-1). We suggest that higher expression of Tim-3 during chronic infection has evolved to limit persistent immune activation and associated tissue damage. These data demonstrate a novel mechanism for Gal-9/Tim-3 interactions to induce resistance of activated CD4(+) T cells to HIV-1 infection and suggest that Gal-9 may play a role in HIV-1 pathogenesis and could be used as a novel microbicide to prevent HIV-1 infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antigen-independent induction of Tim-3 expression on human T cells by the common γ-chain cytokines IL-2, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21 is associated with proliferation and is dependent on the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway.J Immunol. 2012 Apr 15;188(8):3745-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102609. Epub 2012 Mar 14. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22422881
-
Underexpression of TIM-3 and blunted galectin-9-induced apoptosis of CD4+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis.Inflammation. 2012 Apr;35(2):633-7. doi: 10.1007/s10753-011-9355-z. Inflammation. 2012. PMID: 21717191
-
The bitter side of sweet: the role of Galectin-9 in immunopathogenesis of viral infections.Rev Med Virol. 2015 May;25(3):175-86. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1832. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Rev Med Virol. 2015. PMID: 25760439 Review.
-
Interaction between Galectin-9/TIM-3 pathway and follicular helper CD4+ T cells contributes to viral persistence in chronic hepatitis C.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Oct;94:386-393. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.134. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28772217
-
The role of T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 in immune thrombocytopenia.Scand J Immunol. 2014 Apr;79(4):231-6. doi: 10.1111/sji.12153. Scand J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24383985 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the role of galectin-9 and artemin as biomarkers in long COVID with chronic fatigue syndrome: links to inflammation and cognitive function.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 25;15:1443363. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1443363. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39386210 Free PMC article.
-
Negative CD4 + TIM-3 signaling confers resistance against cold preservation damage in mouse liver transplantation.Am J Transplant. 2015 Apr;15(4):954-964. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13067. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Am J Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25676534 Free PMC article.
-
CD71+ Erythroid Cells Exacerbate HIV-1 Susceptibility, Mediate trans-Infection, and Harbor Infective Viral Particles.mBio. 2019 Nov 26;10(6):e02767-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02767-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31772057 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-9 expression defines exhausted T cells and impaired cytotoxic NK cells in patients with virus-associated solid tumors.J Immunother Cancer. 2020 Dec;8(2):e001849. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001849. J Immunother Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33310773 Free PMC article.
-
Galectin-9: From cell biology to complex disease dynamics.J Biosci. 2016 Sep;41(3):507-34. doi: 10.1007/s12038-016-9616-y. J Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27581941 Review.
References
-
- Fauci AS, Johnston MI, Dieffenbach CW, et al. HIV vaccine research: the way forward. Science. 2008;321(5888):530–532. - PubMed
-
- Haase AT. Targeting early infection to prevent HIV-1 mucosal transmission. Nature. 2010;464(7286):217–223. - PubMed
-
- Rerks-Ngarm S, Pitisuttithum P, Nitayaphan S, et al. Vaccination with ALVAC and AIDSVAX to prevent HIV-1 infection in Thailand. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(23):2209–2220. - PubMed
-
- Liu R, Paxton WA, Choe S, et al. Homozygous defect in HIV-1 coreceptor accounts for resistance of some multiply-exposed individuals to HIV-1 infection. Cell. 1996;86(3):367–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

