Mechanism of evenness interrupted (Evi)-exosome release at synaptic boutons
- PMID: 22437826
- PMCID: PMC3351299
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.342667
Mechanism of evenness interrupted (Evi)-exosome release at synaptic boutons
Abstract
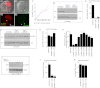
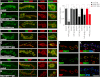
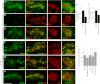
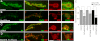
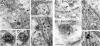
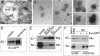
Wnt signaling plays critical roles during synaptic development and plasticity. However, the mechanisms by which Wnts are released and travel to target cells are unresolved. During synaptic development, the secretion of Drosophila Wnt1, Wingless, requires the function of Evenness Interrupted (Evi)/Wls, a Wingless-binding protein that is secreted along with Wingless at the neuromuscular junction. Given that Evi is a transmembrane protein, these studies suggested the presence of a novel vesicular mechanism of trans-synaptic communication, potentially in the form of exosomes. To establish the mechanisms for the release of Evi vesicles, we used a dsRNA assay in cultured cells to screen for genes that when down-regulated prevent the release of Evi vesicles. We identified two proteins, Rab11 and Syntaxin 1A (Syx1A), that were required for Evi vesicle release. To determine whether the same mechanisms were used in vivo at the neuromuscular junction, we altered the activity of Rab11 and Syx1A in motoneurons and determined the impact on Evi release. We found that Syx1A, Rab11, and its effector Myosin5 were required for proper Evi vesicle release. Furthermore, ultrastructural analysis of synaptic boutons demonstrated the presence of multivesicular bodies, organelles involved in the production and release of exosomes, and these multivesicular bodies contained Evi. We also used mass spectrometry, electron microscopy, and biochemical techniques to characterize the exosome fraction from cultured cells. Our studies revealed that secreted Evi vesicles show remarkable conservation with exosomes in other systems. In summary, our observations unravel some of the in vivo mechanisms required for Evi vesicle release.
Figures
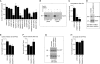
Similar articles
-
Trans-synaptic transmission of vesicular Wnt signals through Evi/Wntless.Cell. 2009 Oct 16;139(2):393-404. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.051. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19837038 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila S2 cells secrete wingless on exosome-like vesicles but the wingless gradient forms independently of exosomes.Traffic. 2013 Jan;14(1):82-96. doi: 10.1111/tra.12016. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Traffic. 2013. PMID: 23035643 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes go with the Wnt.Cell Logist. 2012 Jul 1;2(3):169-173. doi: 10.4161/cl.21981. Cell Logist. 2012. PMID: 23739155 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of SNARE proteins and synaptotagmin I in synaptic transmission: studies at the Drosophila neuromuscular synapse.Neurosignals. 2003 Jan-Feb;12(1):13-30. doi: 10.1159/000068912. Neurosignals. 2003. PMID: 12624525 Review.
-
Synaptic vesicle pools and plasticity of synaptic transmission at the Drosophila synapse.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2004 Dec;47(1-3):18-32. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.05.004. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2004. PMID: 15572160 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Role of Neuron-Glia in Neurological Disorders: At a Glance.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Aug 22;2022:3201644. doi: 10.1155/2022/3201644. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36046684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active Wnt proteins are secreted on exosomes.Nat Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;14(10):1036-45. doi: 10.1038/ncb2574. Epub 2012 Sep 16. Nat Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22983114
-
Exosomal microRNAs as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 8;22(9):4997. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094997. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34066780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of extracellular morphogen gradients: the case for diffusion.Nat Rev Genet. 2021 Jun;22(6):393-411. doi: 10.1038/s41576-021-00342-y. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Nat Rev Genet. 2021. PMID: 33767424 Review.
-
The ESCRT-III Protein CHMP1A Mediates Secretion of Sonic Hedgehog on a Distinctive Subtype of Extracellular Vesicles.Cell Rep. 2018 Jul 24;24(4):973-986.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.06.100. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30044992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnstone R. M. (2005) Revisiting the road to the discovery of exosomes. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 34, 214–219 - PubMed
-
- Nolte-'t Hoen E. N., Buschow S. I., Anderton S. M., Stoorvogel W., Wauben M. H. (2009) Activated T cells recruit exosomes secreted by dendritic cells via LFA-1. Blood 113, 1977–1981 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

