Crystal structure of the µ-opioid receptor bound to a morphinan antagonist
- PMID: 22437502
- PMCID: PMC3523197
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10954
Crystal structure of the µ-opioid receptor bound to a morphinan antagonist
Abstract
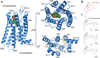
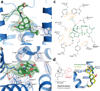
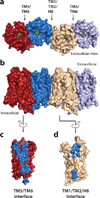
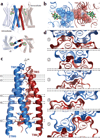
Opium is one of the world's oldest drugs, and its derivatives morphine and codeine are among the most used clinical drugs to relieve severe pain. These prototypical opioids produce analgesia as well as many undesirable side effects (sedation, apnoea and dependence) by binding to and activating the G-protein-coupled µ-opioid receptor (µ-OR) in the central nervous system. Here we describe the 2.8 Å crystal structure of the mouse µ-OR in complex with an irreversible morphinan antagonist. Compared to the buried binding pocket observed in most G-protein-coupled receptors published so far, the morphinan ligand binds deeply within a large solvent-exposed pocket. Of particular interest, the µ-OR crystallizes as a two-fold symmetrical dimer through a four-helix bundle motif formed by transmembrane segments 5 and 6. These high-resolution insights into opioid receptor structure will enable the application of structure-based approaches to develop better drugs for the management of pain and addiction.
Figures

Comment in
-
Structural biology: How opioid drugs bind to receptors.Nature. 2012 May 16;485(7398):314-7. doi: 10.1038/485314a. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22596150 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Structural insights into µ-opioid receptor activation.Nature. 2015 Aug 20;524(7565):315-21. doi: 10.1038/nature14886. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26245379 Free PMC article.
-
Design and synthesis of novel dimeric morphinan ligands for kappa and micro opioid receptors.J Med Chem. 2003 Nov 20;46(24):5162-70. doi: 10.1021/jm030139v. J Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 14613319
-
Characterization of a novel bivalent morphinan possessing kappa agonist and micro agonist/antagonist properties.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Nov;315(2):821-7. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.084343. Epub 2005 Aug 2. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 16076937
-
Morphinan Evolution: The Impact of Advances in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.J Biochem. 2024 Mar 25;175(4):337-355. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvae021. J Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38382631 Review.
-
Recent Chemical and Pharmacological Developments on 14-Oxygenated-N-methylmorphinan-6-ones.Molecules. 2021 Sep 18;26(18):5677. doi: 10.3390/molecules26185677. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34577147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of water in activation mechanism of human N-formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) based on molecular dynamics simulations.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e47114. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047114. Epub 2012 Nov 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23189124 Free PMC article.
-
Mitragynine/Corynantheidine Pseudoindoxyls As Opioid Analgesics with Mu Agonism and Delta Antagonism, Which Do Not Recruit β-Arrestin-2.J Med Chem. 2016 Sep 22;59(18):8381-97. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00748. Epub 2016 Sep 2. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27556704 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric Modulation of GPCRs of Class A by Cholesterol.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 16;22(4):1953. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041953. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A combination of machine learning and infrequent metadynamics to efficiently predict kinetic rates, transition states, and molecular determinants of drug dissociation from G protein-coupled receptors.J Chem Phys. 2020 Sep 28;153(12):124105. doi: 10.1063/5.0019100. J Chem Phys. 2020. PMID: 33003748 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of the OX1R-orexin-A complex suggests two alternative binding modes.BMC Struct Biol. 2015 May 9;15:9. doi: 10.1186/s12900-015-0036-2. BMC Struct Biol. 2015. PMID: 25957175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Katzung BG. Basic and clinical pharmacology. 10th edn. LANGE Mac Graw Hill Medical; 2007.
-
- Matthes HW, et al. Loss of morphine-induced analgesia, reward effect and withdrawal symptoms in mice lacking the mu-opioid-receptor gene. Nature. 1996;383:819–823. - PubMed
-
- Lord JA, Waterfield AA, Hughes J, Kosterlitz HW. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977;267:495–499. - PubMed
-
- Raffa RB, Martinez RP, Connelly CD. G-protein antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotides and mu-opioid supraspinal antinociception. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994;258:R5–R7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

