Hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1 alpha) is induced during reperfusion after renal ischemia and is critical for proximal tubule cell survival
- PMID: 22432008
- PMCID: PMC3303832
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033258
Hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1 alpha) is induced during reperfusion after renal ischemia and is critical for proximal tubule cell survival
Abstract
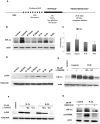
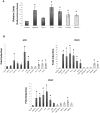
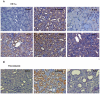
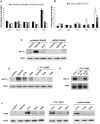
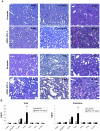
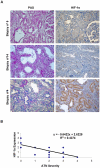
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN) caused by ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) during renal transplantation delays allograft function. Identification of factors that mediate protection and/or epithelium recovery could help to improve graft outcome. We studied the expression, regulation and role of hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1 α), using in vitro and in vivo experimental models of I/R as well as human post-transplant renal biopsies. We found that HIF-1 α is stabilized in proximal tubule cells during ischemia and unexpectedly in late reperfusion, when oxygen tension is normal. Both inductions lead to gene expression in vitro and in vivo. In vitro interference of HIF-1 α promoted cell death and in vivo interference exacerbated tissue damage and renal dysfunction. In pos-transplant human biopsies, HIF-1 α was expressed only in proximal tubules which exhibited normal renal structure with a significant negative correlation with ATN grade. In summary, using experimental models and human biopsies, we identified a novel HIF-1 α induction during reperfusion with a potential critical role in renal transplant.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
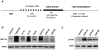
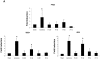

Similar articles
-
Cilastatin Preconditioning Attenuates Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 19;21(10):3583. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103583. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32438631 Free PMC article.
-
miR-127 protects proximal tubule cells against ischemia/reperfusion: identification of kinesin family member 3B as miR-127 target.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044305. Epub 2012 Sep 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22962609 Free PMC article.
-
Proximal tubular FHL2, a novel downstream target of hypoxia inducible factor 1, is a protector against ischemic acute kidney injury.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 May 30;81(1):244. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05289-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38814462 Free PMC article.
-
The role of hypoxia-inducible factors in organ donation and transplantation: the current perspective and future opportunities.Am J Transplant. 2014 Jul;14(7):1481-7. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12737. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Am J Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24909061 Review.
-
The Intriguing Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor in Myocardial Ischemia and Reperfusion: A Comprehensive Review.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 May 14;10(5):215. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10050215. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 37233182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional Coactivator and Chromatin Protein PC4 Is Involved in Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Spatial Memory Extinction.J Biol Chem. 2016 Sep 23;291(39):20303-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.744169. Epub 2016 Jul 28. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27471272 Free PMC article.
-
Fatty acid binding protein-4 (FABP4) is a hypoxia inducible gene that sensitizes mice to liver ischemia/reperfusion injury.J Hepatol. 2015 Oct;63(4):855-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.030. Epub 2015 Jun 10. J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26070408 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of Primary Human Hippocampal Astrocyte Cell Culture Following Exposure to Hypoxia.Malays J Med Sci. 2023 Feb;30(1):92-106. doi: 10.21315/mjms2023.30.1.8. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Malays J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36875187 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory role of HIF-1 in tubular epithelial cells in response to kidney injury.Histol Histopathol. 2020 Apr;35(4):321-330. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-182. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Histol Histopathol. 2020. PMID: 31691948 Review.
-
Roxadustat for Patients with Posttransplant Anemia: A Narrative Review.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2023 Nov 10;10(1):32-38. doi: 10.1159/000535071. eCollection 2024 Feb. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38322628 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kellum JA. Acute kidney injury. Crit Care Med. 2008;36(4 Suppl):S141–5. - PubMed
-
- Ojo AO, Wolfe RA, Held PJ, Port FK, Schmouder RL. Delayed graft function: risk factors and implications for renal allograft survival. Transplantation. 1997;15; 63(7):968–74. - PubMed
-
- Semenza GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: oxygen homeostasis and disease pathohysiology. Trends Mol Med. 2001;7(8):345–50. - PubMed
-
- Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D, Laughner E, Hanrahan, et al. Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res. 2000;60(6):1541–5. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Schmid T, Frank R, Brüne B. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling controls levels of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(14):13506–13. - PubMed

