Profound depletion of host conventional dendritic cells, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, and B cells does not prevent graft-versus-host disease induction
- PMID: 22422880
- PMCID: PMC3324629
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102795
Profound depletion of host conventional dendritic cells, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, and B cells does not prevent graft-versus-host disease induction
Abstract
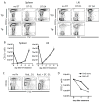
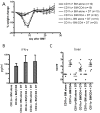
The efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is limited by graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Host hematopoietic APCs are important initiators of GVHD, making them logical targets for GVHD prevention. Conventional dendritic cells (DCs) are key APCs for T cell responses in other models of T cell immunity, and they are sufficient for GVHD induction. However, we report in this article that in two polyclonal GVHD models in which host hematopoietic APCs are essential, GVHD was not decreased when recipient conventional DCs were inducibly or constitutively deleted. Additional profound depletion of plasmacytoid DCs and B cells, with or without partial depletion of CD11b(+) cells, also did not ameliorate GVHD. These data indicate that, in contrast with pathogen models, there is a surprising redundancy as to which host cells can initiate GVHD. Alternatively, very low numbers of targeted APCs were sufficient. We hypothesize the difference in APC requirements in pathogen and GVHD models relates to the availability of target Ags. In antipathogen responses, specialized APCs are uniquely equipped to acquire and present exogenous Ags, whereas in GVHD, all host cells directly present alloantigens. These studies make it unlikely that reagent-based host APC depletion will prevent GVHD in the clinic.
Figures

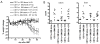

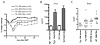
Similar articles
-
Recipient B cells are not required for graft-versus-host disease induction.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010 Sep;16(9):1222-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2010.03.015. Epub 2010 Mar 23. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010. PMID: 20338255 Free PMC article.
-
Host dendritic cells alone are sufficient to initiate acute graft-versus-host disease.J Immunol. 2004 Jun 15;172(12):7393-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7393. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15187116
-
Induction of acute GVHD by sex-mismatched H-Y antigens in the absence of functional radiosensitive host hematopoietic-derived antigen-presenting cells.Blood. 2012 Apr 19;119(16):3844-53. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-10-384057. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22101894 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstructing immunity after allogeneic transplantation.Immunol Res. 2004;29(1-3):269-82. doi: 10.1385/IR:29:1-3:269. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15181288 Review.
-
Acute graft-vs-host disease: pathobiology and management.Exp Hematol. 2001 Mar;29(3):259-77. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(00)00677-9. Exp Hematol. 2001. PMID: 11274753 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunopathological mechanisms and clinical manifestations of ocular graft-versus-host disease following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024 Aug;59(8):1049-1056. doi: 10.1038/s41409-024-02321-3. Epub 2024 May 31. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38822141 Review.
-
T cell exhaustion and a failure in antigen presentation drive resistance to the graft-versus-leukemia effect.Nat Commun. 2020 Aug 24;11(1):4227. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17991-y. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32839441 Free PMC article.
-
Concise review: acute graft-versus-host disease: immunobiology, prevention, and treatment.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013 Jan;2(1):25-32. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2012-0115. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013. PMID: 23283494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of Human Regulatory Dendritic Cells from Cryopreserved Healthy Donor Cells and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients.Cells. 2023 Sep 28;12(19):2372. doi: 10.3390/cells12192372. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830587 Free PMC article.
-
Siglec-G-CD24 axis controls the severity of graft-versus-host disease in mice.Blood. 2014 May 29;123(22):3512-23. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-12-545335. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24695850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shlomchik WD. Graft-versus-host disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:340–352. - PubMed
-
- Teshima T, Ordemann R, Reddy P, Gagin S, Liu C, Cooke KR, Ferrara JL. Acute graft-versus-host disease does not require alloantigen expression on host epithelium. Nat Med. 2002;8:575–581. - PubMed
-
- Duffner UA, Maeda Y, Cooke KR, Reddy P, Ordemann R, Liu C, Ferrara JL, Teshima T. Host dendritic cells alone are sufficient to initiate acute graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol. 2004;172:7393–7398. - PubMed
-
- Koyama M, Hashimoto D, Aoyama K, Matsuoka K, Karube K, Niiro H, Harada M, Tanimoto M, Akashi K, Teshima T. Plasmacytoid dendritic cells prime alloreactive T cells to mediate graft-versus-host disease as antigen-presenting cells. Blood. 2009;113:2088–2095. - PubMed
-
- Matte CC, Liu J, Cormier J, Anderson BE, Athanasiadis I, Jain D, McNiff J, Shlomchik WD. Donor APCs are required for maximal GVHD but not for GVL. Nat Med. 2004;10:987–992. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

