A multimodal RAGE-specific inhibitor reduces amyloid β-mediated brain disorder in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 22406537
- PMCID: PMC3314449
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI58642
A multimodal RAGE-specific inhibitor reduces amyloid β-mediated brain disorder in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease
Abstract
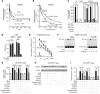
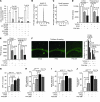
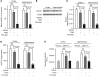
In Alzheimer disease (AD), amyloid β peptide (Aβ) accumulates in plaques in the brain. Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) mediates Aβ-induced perturbations in cerebral vessels, neurons, and microglia in AD. Here, we identified a high-affinity RAGE-specific inhibitor (FPS-ZM1) that blocked Aβ binding to the V domain of RAGE and inhibited Aβ40- and Aβ42-induced cellular stress in RAGE-expressing cells in vitro and in the mouse brain in vivo. FPS-ZM1 was nontoxic to mice and readily crossed the blood-brain barrier (BBB). In aged APPsw/0 mice overexpressing human Aβ-precursor protein, a transgenic mouse model of AD with established Aβ pathology, FPS-ZM1 inhibited RAGE-mediated influx of circulating Aβ40 and Aβ42 into the brain. In brain, FPS-ZM1 bound exclusively to RAGE, which inhibited β-secretase activity and Aβ production and suppressed microglia activation and the neuroinflammatory response. Blockade of RAGE actions at the BBB and in the brain reduced Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels in brain markedly and normalized cognitive performance and cerebral blood flow responses in aged APPsw/0 mice. Our data suggest that FPS-ZM1 is a potent multimodal RAGE blocker that effectively controls progression of Aβ-mediated brain disorder and that it may have the potential to be a disease-modifying agent for AD.
Figures
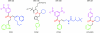
Comment in
-
Neurodegenerative disease: Taming the RAGE of Alzheimer's disease.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 May;11(5):351. doi: 10.1038/nrd3727. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22685712 No abstract available.
-
Amyloid β-peptide and Alzheimers disease: it's all the RAGE.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012 Aug;11(5):494. doi: 10.2174/187152712801661275. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22691133 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Targeted inhibition of RAGE reduces amyloid-β influx across the blood-brain barrier and improves cognitive deficits in db/db mice.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Mar 15;131:143-153. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.12.026. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29248482
-
Effects of RAGE-Specific Inhibitor FPS-ZM1 on Amyloid-β Metabolism and AGEs-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rat Hippocampus.Neurochem Res. 2016 May;41(5):1192-9. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1814-8. Epub 2016 Jan 6. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 26738988
-
RAGE mediates Aβ accumulation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease via modulation of β- and γ-secretase activity.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Mar 15;27(6):1002-1014. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy017. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29329433 Free PMC article.
-
Preventing activation of receptor for advanced glycation endproducts in Alzheimer's disease.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2005 Jun;4(3):249-66. doi: 10.2174/1568007054038210. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2005. PMID: 15975028 Review.
-
RAGE: a potential target for Abeta-mediated cellular perturbation in Alzheimer's disease.Curr Mol Med. 2007 Dec;7(8):735-42. doi: 10.2174/156652407783220741. Curr Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 18331231 Review.
Cited by
-
Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease.Nat Rev Neurol. 2015 Aug;11(8):457-70. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.119. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26195256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of the HMGB1/RAGE axis protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity via suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jan 1;20(2):784-800. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.82003. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38169643 Free PMC article.
-
Receptors on Microglia.Adv Neurobiol. 2024;37:83-121. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-55529-9_6. Adv Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39207688 Review.
-
Adaptor protein MyD88 confers the susceptibility to stress via amplifying immune danger signals.Brain Behav Immun. 2023 Feb;108:204-220. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2022.12.007. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Brain Behav Immun. 2023. PMID: 36496170 Free PMC article.
-
Reconsidering the role of blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer's disease: From delivery to target.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Feb 16;15:1102809. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1102809. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36875694 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297(5580):353–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

