Anti-idiotypic antibody specific to GAD65 autoantibody prevents type 1 diabetes in the NOD mouse
- PMID: 22384267
- PMCID: PMC3286479
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032515
Anti-idiotypic antibody specific to GAD65 autoantibody prevents type 1 diabetes in the NOD mouse
Abstract
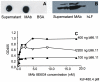
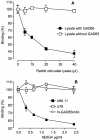
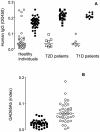
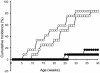
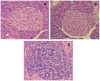
Overt autoantibodies to the smaller isoform of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD65Ab) are a characteristic in patients with Type 1 diabetes (T1D). Anti-idiotypic antibodies (anti-Id) directed to GAD65Ab effectively prevent the binding of GAD65 to GAD65Ab in healthy individuals. Levels of GAD65Ab-specific anti-Id are significantly lower in patients with T1D, leading to overt GAD65Ab in these patients. To determine the possible protective role of GAD65Ab-specific anti-Id in T1D pathogenesis, we developed the monoclonal anti-Id MAb 8E6G4 specifically targeting human monoclonal GAD65Ab b96.11. MAb 8E6G4 was demonstrated as a specific anti-Id directed to the antigen binding site of b96.11. MAb 8E6G4 recognized human antibodies in sera from healthy individuals, T2D patients, and T1D patients as established by ELISA. We confirmed these MAb 8E6G4-bound human antibodies to contain GAD65Ab by testing the eluted antibodies for binding to GAD65 in radioligand binding assays. These findings confirm that GAD65Ab are present in sera of individuals, who test GAD65Ab-negative in conventional detection assays. To test our hypothesis that GAD65Ab-specific anti-Id have an immune modulatory role in T1D, we injected young Non Obese Diabetic (NOD) mice with MAb 8E6G4. The animals were carefully monitored for development of T1D for 40 weeks. Infiltration of pancreatic islets by mononuclear cells (insulitis) was determined to establish the extent of an autoimmune attack on the pancreatic islets. Administration of MAb 8E6G4 significantly reduced the cumulative incidence rate of T1D and delayed the time of onset. Insulitis was significantly less severe in animals that received MAb 8E6G4 as compared to control animals. These results support our hypothesis that anti-Id specific to GAD65Ab have a protective role in T1D.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunoglobulin subclass profiles of anti-idiotypic antibodies to GAD65Ab differ between type 1 diabetes patients and healthy individuals.Scand J Immunol. 2011 Oct;74(4):363-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2011.02565.x. Scand J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21517929 Free PMC article.
-
Decline in titers of anti-idiotypic antibodies specific to autoantibodies to GAD65 (GAD65Ab) precedes development of GAD65Ab and type 1 diabetes.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 13;8(6):e65173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065173. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23785410 Free PMC article.
-
The lack of anti-idiotypic antibodies, not the presence of the corresponding autoantibodies to glutamate decarboxylase, defines type 1 diabetes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 8;105(14):5471-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0800578105. Epub 2008 Mar 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18367670 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of anti-idiotypic antibodies in autoimmunity--lessons for type 1 diabetes.Autoimmunity. 2012 Jun;45(4):320-31. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2012.659299. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Autoimmunity. 2012. PMID: 22288464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GAD65 autoimmunity-clinical studies.Adv Immunol. 2008;100:39-78. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)00803-1. Adv Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19111163 Review.
Cited by
-
Altered immune regulation in type 1 diabetes.Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:254874. doi: 10.1155/2013/254874. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24285974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory potential of anti-idiotypic antibodies for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.Future Sci OA. 2020 Oct 29;7(2):FSO648. doi: 10.2144/fsoa-2020-0142. Future Sci OA. 2020. PMID: 33437514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B Cell in Autoimmune Diseases.Scientifica (Cairo). 2012;2012:215308. doi: 10.6064/2012/215308. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012. PMID: 23807906 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the cellular immunological pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 May;18(5):749-58. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12270. Epub 2014 Mar 14. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24629100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of dendritic cells and T lymphocytes for the therapeutic effect of Dangguiliuhuang decoction to autoimmune diabetes.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 11;5:13982. doi: 10.1038/srep13982. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26358493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanjeevi CB, Falorni A, Robertson J, Lernmark A. Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Nutrition & Metabolism. 1996;9:167–182.
-
- Jerne NK. Towards a network theory of the immune system. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1974;125C:373–389. - PubMed
-
- Anderson CJ, Neas BR, Pan Z, Taylor-Albert E, Reichlin M, et al. The presence of masked antiribosomal P autoantibodies in healthy children. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:33–40. - PubMed
-
- Stafford HA, Anderson CJ, Reichlin M. Unmasking of anti-ribosomal P autoantibodies in healthy individuals. J Immunol. 1995;155:2754–2761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

