Identification of nucleotide patterns enriched in secreted RNAs as putative cis-acting elements targeting them to exosome nano-vesicles
- PMID: 22369587
- PMCID: PMC3333177
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-S3-S18
Identification of nucleotide patterns enriched in secreted RNAs as putative cis-acting elements targeting them to exosome nano-vesicles
Abstract
Background: Exosomes are nanoscale membrane vesicles released by most cells. They are postulated to be involved in cell-cell communication and genetic reprogramming of their target cells. In addition to proteins and lipids, they release RNA molecules many of which are not present in the donor cells implying a highly selective mode of their packaging into these vesicles. Sequence motifs targeting RNA to the vesicles are currently unknown.
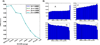
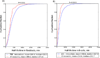
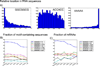
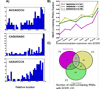
Results: Ab initio approach was applied for computational identification of potential RNA secretory motifs in the primary sequences of exosome-enriched RNAs (eRNAs). Exhaustive motif analysis for the first time revealed unique sequence features of eRNAs. We discovered multiple linear motifs specifically enriched in secreted RNAs. Their potential function as cis-acting elements targeting RNAs to exosomes is proposed. The motifs co-localized in the same transcripts suggesting combinatorial organization of these secretory signals. We investigated associations of the discovered motifs with other RNA parameters. Secreted RNAs were found to have almost twice shorter half-life times on average, in comparison with cytoplasmic RNAs, and the occurrence of some eRNA-specific motifs significantly correlated with this eRNA feature. Also, we found that eRNAs are highly enriched in long noncoding RNAs.
Conclusions: Secreted RNAs share specific sequence motifs that may potentially function as cis-acting elements targeting RNAs to exosomes. Discovery of these motifs will be useful for our understanding the roles of eRNAs in cell-cell communication and genetic reprogramming of the target cells. It will also facilitate nano-scale vesicle engineering and selective targeting of RNAs of interest to these vesicles for gene therapy purposes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of RNA Motifs in RNA Interaction with Membrane Lipid Rafts: Implications for Therapeutic Applications of Exosomal RNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 30;22(17):9416. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179416. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502324 Free PMC article.
-
Cytosolic YB-1 and NSUN2 are the only proteins recognizing specific motifs present in mRNAs enriched in exosomes.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2017 Jun;1865(6):664-673. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2017.03.010. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2017. PMID: 28341602
-
Exploring the RNA landscape of endothelial exosomes.RNA. 2018 Mar;24(3):423-435. doi: 10.1261/rna.064352.117. Epub 2017 Dec 27. RNA. 2018. PMID: 29282313 Free PMC article.
-
Horizontal transfer of RNAs: exosomes as mediators of intercellular communication.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012 Mar-Apr;3(2):286-93. doi: 10.1002/wrna.115. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2012. PMID: 22012863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane-bound extracellular vesicles secreted by parasitic protozoa: cellular structures involved in the communication between cells.Parasitol Res. 2020 Jul;119(7):2005-2023. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06691-7. Epub 2020 May 12. Parasitol Res. 2020. PMID: 32394001 Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomes secreted by human cells transport largely mRNA fragments that are enriched in the 3'-untranslated regions.Biol Direct. 2013 Jun 7;8:12. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-8-12. Biol Direct. 2013. PMID: 23758897 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNAs: a potential novel class of cancer biomarkers.Front Genet. 2015 Apr 23;6:145. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00145. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25954300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes as carriers transporting long non‑coding RNAs: Molecular characteristics and their function in cancer (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2019 Aug;20(2):851-862. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10340. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31173220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reorganization of the Landscape of Translated mRNAs in NSUN2-Deficient Cells and Specific Features of NSUN2 Target mRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 28;23(17):9740. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179740. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077143 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome for mRNA delivery: strategies and therapeutic applications.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 4;22(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02634-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38965553 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

