Photoperiod- and thermo-sensitive genic male sterility in rice are caused by a point mutation in a novel noncoding RNA that produces a small RNA
- PMID: 22349461
- PMCID: PMC3317565
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2012.28
Photoperiod- and thermo-sensitive genic male sterility in rice are caused by a point mutation in a novel noncoding RNA that produces a small RNA
Abstract
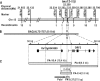
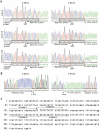
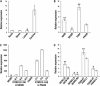
Photoperiod- and thermo-sensitive genic male sterility (PGMS and TGMS) are the core components for hybrid breeding in crops. Hybrid rice based on the two-line system using PGMS and TGMS lines has been successfully developed and applied widely in agriculture. However, the molecular mechanism underlying the control of PGMS and TGMS remains obscure. In this study, we mapped and cloned a major locus, p/tms12-1 (photo- or thermo-sensitive genic male sterility locus on chromosome 12), which confers PGMS in the japonica rice line Nongken 58S (NK58S) and TGMS in the indica rice line Peiai 64S (PA64S, derived from NK58S). A 2.4-kb DNA fragment containing the wild-type allele P/TMS12-1 was able to restore the pollen fertility of NK58S and PA64S plants in genetic complementation. P/TMS12-1 encodes a unique noncoding RNA, which produces a 21-nucleotide small RNA that we named osa-smR5864w. A substitution of C-to-G in p/tms12-1, the only polymorphism relative to P/TMS12-1, is present in the mutant small RNA, namely osa-smR5864m. Furthermore, overexpression of a 375-bp sequence of P/TMS12-1 in transgenic NK58S and PA64S plants also produced osa-smR5864w and restored pollen fertility. The small RNA was expressed preferentially in young panicles, but its expression was not markedly affected by different day lengths or temperatures. Our results reveal that the point mutation in p/tms12-1, which probably leads to a loss-of-function for osa-smR5864m, constitutes a common cause for PGMS and TGMS in the japonica and indica lines, respectively. Our findings thus suggest that this noncoding small RNA gene is an important regulator of male development controlled by cross-talk between the genetic networks and environmental conditions.
Figures

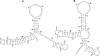
Similar articles
-
Genetic and molecular characterization of photoperiod and thermo-sensitive male sterility in rice.Plant Reprod. 2018 Mar;31(1):3-14. doi: 10.1007/s00497-017-0310-5. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Plant Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29094211 Review.
-
Molecular mapping of two reverse photoperiod-sensitive genic male sterility genes (rpms1 and rpms2) in rice (Oryza sativa L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2008 Dec;118(1):77-83. doi: 10.1007/s00122-008-0877-1. Epub 2008 Sep 23. Theor Appl Genet. 2008. PMID: 18810384
-
Development and validation of a functional co-dominant SNP marker for the photoperiod thermo-sensitive genic male sterility pms3 (p/tms12-1) gene in rice.Breed Sci. 2017 Dec;67(5):535-539. doi: 10.1270/jsbbs.16138. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Breed Sci. 2017. PMID: 29398948 Free PMC article.
-
Jasmonic Acid Plays a Pivotal Role in Pollen Development and Fertility Regulation in Different Types of P(T)GMS Rice Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 25;22(15):7926. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157926. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360691 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs and plant male sterility: current knowledge and future prospects.Plant Cell Rep. 2018 Feb;37(2):177-191. doi: 10.1007/s00299-018-2248-y. Epub 2018 Jan 13. Plant Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29332167 Review.
Cited by
-
Global identification of Arabidopsis lncRNAs reveals the regulation of MAF4 by a natural antisense RNA.Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 29;9(1):5056. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07500-7. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30498193 Free PMC article.
-
Role of methylation in vernalization and photoperiod pathway: a potential flowering regulator?Hortic Res. 2023 Aug 29;10(10):uhad174. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhad174. eCollection 2023 Oct. Hortic Res. 2023. PMID: 37841501 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis and regulatory hierarchy of phased small interfering RNAs in plants.Plant Biotechnol J. 2018 May;16(5):965-975. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12882. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Plant Biotechnol J. 2018. PMID: 29327403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis of diverse plant phasiRNAs involves an miRNA-trigger and Dicer-processing.J Plant Res. 2017 Jan;130(1):17-23. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0878-0. Epub 2016 Nov 29. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 27900550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of phased small interfering RNA genes in response to Botrytis cinerea infection in Solanum lycopersicum.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 8;7(1):3019. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02233-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28596514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin SC, Yuan LP.Hybrid rice breeding in China In: Innovative approaches to rice breeding. Manila, Philippines: International Rice Research Institute, 198035–52.
-
- Yuan LP. Purification and production of foundation seed of rice PGMS and TGMS lines. Hybrid Rice. 1994;6:1–3.
-
- Yang Q, Liang C, Zhuang W, et al. Characterization and identification of the candidate gene of rice thermo-sensitive genic male sterile gene tms5 by mapping. Planta. 2007;225:321–330. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

