Understanding the cooperative interaction between myosin II and actin cross-linkers mediated by actin filaments during mechanosensation
- PMID: 22339860
- PMCID: PMC3260782
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.12.020
Understanding the cooperative interaction between myosin II and actin cross-linkers mediated by actin filaments during mechanosensation
Abstract
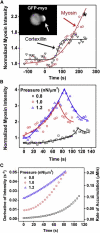
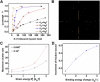
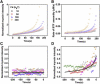
Myosin II is a central mechanoenzyme in a wide range of cellular morphogenic processes. Its cellular localization is dependent not only on signal transduction pathways, but also on mechanical stress. We suggest that this stress-dependent distribution is the result of both the force-dependent binding to actin filaments and cooperative interactions between bound myosin heads. By assuming that the binding of myosin heads induces and/or stabilizes local conformational changes in the actin filaments that enhances myosin II binding locally, we successfully simulate the cooperative binding of myosin to actin observed experimentally. In addition, we can interpret the cooperative interactions between myosin and actin cross-linking proteins observed in cellular mechanosensation, provided that a similar mechanism operates among different proteins. Finally, we present a model that couples cooperative interactions to the assembly dynamics of myosin bipolar thick filaments and that accounts for the transient behaviors of the myosin II accumulation during mechanosensation. This mechanism is likely to be general for a range of myosin II-dependent cellular mechanosensory processes.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mechanosensing through cooperative interactions between myosin II and the actin crosslinker cortexillin I.Curr Biol. 2009 Sep 15;19(17):1421-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.07.018. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19646871 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin heavy-chain kinase A from Dictyostelium possesses a novel actin-binding domain that cross-links actin filaments.Biochem J. 2006 Apr 15;395(2):373-83. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051376. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16372899 Free PMC article.
-
A mechanosensory system governs myosin II accumulation in dividing cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Apr;23(8):1510-23. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-07-0601. Epub 2012 Feb 29. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22379107 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of myosin II in Dictyostelium.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Sep;85(9-10):969-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.04.004. Epub 2006 Jun 30. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16814425 Review.
-
Biochemistry of Drebrin and Its Binding to Actin Filaments.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1006:37-47. doi: 10.1007/978-4-431-56550-5_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28865013 Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokinesis mechanics and mechanosensing.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012 Oct;69(10):700-9. doi: 10.1002/cm.21045. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22761196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneity in The Mechanical Properties of Integrins Determines Mechanotransduction Dynamics in Bone Osteoblasts.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 11;9(1):13113. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47958-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31511609 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical stress induces a scalable switch in cortical flow polarization during cytokinesis.J Cell Sci. 2019 Oct 9;132(19):jcs231357. doi: 10.1242/jcs.231357. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31519810 Free PMC article.
-
Actin dynamics and competition for myosin monomer govern the sequential amplification of myosin filaments.Nat Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;19(2):85-93. doi: 10.1038/ncb3463. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Nat Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28114272 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of myosin IIA and filamentous actin during insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Exp Cell Res. 2014 Mar 10;322(1):81-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.12.011. Epub 2013 Dec 25. Exp Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24374234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spudich J.A. The myosin swinging cross-bridge model. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001;2:387–392. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

