Akt inhibitors MK-2206 and nelfinavir overcome mTOR inhibitor resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 22338016
- PMCID: PMC3889476
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1407
Akt inhibitors MK-2206 and nelfinavir overcome mTOR inhibitor resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
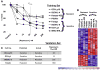
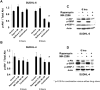
Purpose: The mTOR pathway is constitutively activated in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). mTOR inhibitors have activity in DLBCL, although response rates remain low. We evaluated DLBCL cell lines with differential resistance to the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin: (i) to identify gene expression profile(s) (GEP) associated with resistance to rapamycin, (ii) to understand mechanisms of rapamycin resistance, and (iii) to identify compounds likely to synergize with mTOR inhibitor.
Experimental design: We sought to identify a GEP of mTOR inhibitor resistance by stratification of eight DLBCL cell lines with respect to response to rapamycin. Then, using pathway analysis and connectivity mapping, we sought targets likely accounting for this resistance and compounds likely to overcome it. We then evaluated two compounds thus identified for their potential to synergize with rapamycin in DLBCL and confirmed mechanisms of activity with standard immunoassays.
Results: We identified a GEP capable of reliably distinguishing rapamycin-resistant from rapamycin-sensitive DLBCL cell lines. Pathway analysis identified Akt as central to the differentially expressed gene network. Connectivity mapping identified compounds targeting Akt as having a high likelihood of reversing the GEP associated with mTOR inhibitor resistance. Nelfinavir and MK-2206, chosen for their Akt-inhibitory properties, yielded synergistic inhibition of cell viability in combination with rapamycin in DLBCL cell lines, and potently inhibited phosphorylation of Akt and downstream targets of activated mTOR.
Conclusions: GEP identifies DLBCL subsets resistant to mTOR inhibitor therapy. Combined targeting of mTOR and Akt suppresses activation of key components of the Akt/mTOR pathway and results in synergistic cytotoxicity. These findings are readily adaptable to clinical trials.
©2012 AACR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phospho-p70S6K/p85S6K and cdc2/cdk1 are novel targets for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma combination therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 1;15(5):1708-20. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1543. Epub 2009 Feb 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19223503
-
Inhibition of histone deacetylase overcomes rapamycin-mediated resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by inhibiting Akt signaling through mTORC2.Blood. 2009 Oct 1;114(14):2926-35. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-05-220889. Epub 2009 Jul 29. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19641186 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: clinical significance and inhibitory effect of rituximab.Ann Hematol. 2013 Oct;92(10):1351-8. doi: 10.1007/s00277-013-1770-9. Epub 2013 May 2. Ann Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23636313
-
Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: current knowledge and clinical significance.Molecules. 2014 Sep 11;19(9):14304-15. doi: 10.3390/molecules190914304. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25215588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New inhibitors of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway: insights into mTOR signaling from a new generation of Tor Kinase Domain Inhibitors (TORKinibs).Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;347:241-62. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_64. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20549474 Review.
Cited by
-
Renin-angiotensin system inhibitor attenuates oxidative stress induced human coronary artery endothelial cell dysfunction via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Jan;15(1):152-164. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2018.74026. Epub 2018 Mar 8. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30697266 Free PMC article.
-
Differential roles of ERRFI1 in EGFR and AKT pathway regulation affect cancer proliferation.EMBO Rep. 2018 Mar;19(3):e44767. doi: 10.15252/embr.201744767. Epub 2018 Jan 15. EMBO Rep. 2018. PMID: 29335246 Free PMC article.
-
Vertical inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway is synergistic in breast cancer.Oncogenesis. 2017 Oct 9;6(10):e385. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2017.86. Oncogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28991258 Free PMC article.
-
Phase II study of an AKT inhibitor MK2206 in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma.Br J Haematol. 2015 Nov;171(4):463-70. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13603. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 26213141 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Identification of Prognostic Model and Biomarkers for Cancer Stem Cell Characteristics in Glioblastoma by Network Analysis of Multi-Omics Data and Stemness Indices.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 19;8:558961. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.558961. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P, et al. The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood. 2007;109:1857–61. - PubMed
-
- Hudes G, Carducci M, Tomczak P, Dutcher J, Figlin R, Kapoor A, et al. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2271–81. - PubMed
-
- Hess G, Herbrecht R, Romaguera J, Verhoef G, Crump M, Gisselbrecht C, et al. Phase III study to evaluate temsirolimus compared with investigator's choice therapy for the treatment of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3822–9. - PubMed
-
- Hess G, Smith SM, Berkenblit A, Coiffier B. Temsirolimus in mantle cell lymphoma and other non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. Semin Oncol. 2009;36(3):S37–45. - PubMed
-
- Sehgal SN. Rapamune (Sirolimus, rapamycin): an overview and mechanism of action. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. 1995;17:660–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

