Thymine DNA glycosylase specifically recognizes 5-carboxylcytosine-modified DNA
- PMID: 22327402
- PMCID: PMC3307914
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.914
Thymine DNA glycosylase specifically recognizes 5-carboxylcytosine-modified DNA
Abstract
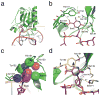
Human thymine DNA glycosylase (hTDG) efficiently excises 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC), a key oxidation product of 5-methylcytosine in genomic DNA, in a recently discovered cytosine demethylation pathway. We present here the crystal structures of the hTDG catalytic domain in complex with duplex DNA containing either 5caC or a fluorinated analog. These structures, together with biochemical and computational analyses, reveal that 5caC is specifically recognized in the active site of hTDG, supporting the role of TDG in mammalian 5-methylcytosine demethylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural Basis for Excision of 5-Formylcytosine by Thymine DNA Glycosylase.Biochemistry. 2016 Nov 15;55(45):6205-6208. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00982. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27805810 Free PMC article.
-
Excision of 5-hydroxymethyluracil and 5-carboxylcytosine by the thymine DNA glycosylase domain: its structural basis and implications for active DNA demethylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Nov 1;40(20):10203-14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks845. Epub 2012 Sep 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22962365 Free PMC article.
-
Activity and crystal structure of human thymine DNA glycosylase mutant N140A with 5-carboxylcytosine DNA at low pH.DNA Repair (Amst). 2013 Jul;12(7):535-40. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 May 13. DNA Repair (Amst). 2013. PMID: 23680598 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and mutation studies of two DNA demethylation related glycosylases: MBD4 and TDG.Biophysics (Nagoya-shi). 2014 Oct 18;10:63-8. doi: 10.2142/biophysics.10.63. eCollection 2014. Biophysics (Nagoya-shi). 2014. PMID: 27493500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modifications in DNA could mimic oxidative DNA damage: A double-edged sword.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Aug;32:52-57. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.04.013. Epub 2015 May 1. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25956859 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular basis of an atypical dsDNA 5mC/6mA bifunctional dioxygenase CcTet from Coprinopsis cinerea in catalyzing dsDNA 5mC demethylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Apr 24;52(7):3886-3895. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae066. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38324471 Free PMC article.
-
Base-resolution analysis of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in the mammalian genome.Cell. 2012 Jun 8;149(6):1368-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.027. Epub 2012 May 17. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22608086 Free PMC article.
-
5-methylcytosine-sensitive variants of Thermococcus kodakaraensis DNA polymerase.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Nov 16;44(20):9881-9890. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw812. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27651460 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Function of TET Enzymes.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1389:239-267. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-11454-0_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36350513
-
Enhanced CRISPR-based DNA demethylation by Casilio-ME-mediated RNA-guided coupling of methylcytosine oxidation and DNA repair pathways.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 20;10(1):4296. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12339-7. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31541098 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

