Insulin and insulin-like growth factor II differentially regulate endocytic sorting and stability of insulin receptor isoform A
- PMID: 22318726
- PMCID: PMC3322853
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.252478
Insulin and insulin-like growth factor II differentially regulate endocytic sorting and stability of insulin receptor isoform A
Abstract
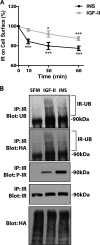
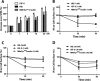
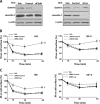
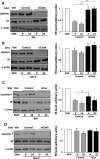
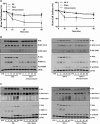
The insulin receptor isoform A (IR-A) binds both insulin and insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-II, although the affinity for IGF-II is 3-10-fold lower than insulin depending on a cell and tissue context. Notably, in mouse embryonic fibroblasts lacking the IGF-IR and expressing solely the IR-A (R-/IR-A), IGF-II is a more potent mitogen than insulin. As receptor endocytosis and degradation provide spatial and temporal regulation of signaling events, we hypothesized that insulin and IGF-II could affect IR-A biological responses by differentially regulating IR-A trafficking. Using R-/IR-A cells, we discovered that insulin evoked significant IR-A internalization, a process modestly affected by IGF-II. However, the differential internalization was not due to IR-A ubiquitination. Notably, prolonged stimulation of R-/IR-A cells with insulin, but not with IGF-II, targeted the receptor to a degradative pathway. Similarly, the docking protein insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) was down-regulated after prolonged insulin but not IGF-II exposure. Similar results were also obtained in experiments using [NMeTyr(B26)]-insulin, an insulin analog with IR-A binding affinity similar to IGF-II. Finally, we discovered that IR-A was internalized through clathrin-dependent and -independent pathways, which differentially regulated the activation of downstream effectors. Collectively, our results suggest that a lower affinity of IGF-II for the IR-A promotes lower IR-A phosphorylation and activation of early downstream effectors vis à vis insulin but may protect IR-A and IRS-1 from down-regulation thereby evoking sustained and robust mitogenic stimuli.
Figures
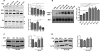

Similar articles
-
Differential signaling activation by insulin and insulin-like growth factors I and II upon binding to insulin receptor isoform A.Endocrinology. 2009 Aug;150(8):3594-602. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0377. Epub 2009 May 14. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19443570
-
Decorin differentially modulates the activity of insulin receptor isoform A ligands.Matrix Biol. 2014 Apr;35:82-90. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.12.010. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Matrix Biol. 2014. PMID: 24389353 Free PMC article.
-
Differential gene expression induced by insulin and insulin-like growth factor-II through the insulin receptor isoform A.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 24;278(43):42178-89. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304980200. Epub 2003 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12881524
-
Targeted gene mutations define the roles of insulin and IGF-I receptors in mouse embryonic development.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1999 Jul-Aug;12(4):475-85. doi: 10.1515/jpem.1999.12.4.475. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1999. PMID: 10417963 Review.
-
Insulin-like Growth Factor-2 (IGF-2) in Fibrosis.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 25;12(11):1557. doi: 10.3390/biom12111557. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatocyte Deletion of IGF2 Prevents DNA Damage and Tumor Formation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Jul;9(21):e2105120. doi: 10.1002/advs.202105120. Epub 2022 May 26. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35615981 Free PMC article.
-
Ephrin-B2 controls PDGFRβ internalization and signaling.Genes Dev. 2013 Dec 1;27(23):2576-89. doi: 10.1101/gad.224089.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 24298057 Free PMC article.
-
Rational steering of insulin binding specificity by intra-chain chemical crosslinking.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 21;6:19431. doi: 10.1038/srep19431. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26792393 Free PMC article.
-
Structural integrity of the B24 site in human insulin is important for hormone functionality.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 12;288(15):10230-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.448050. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23447530 Free PMC article.
-
Dichotomy of decorin activity on the insulin-like growth factor-I system.FEBS J. 2013 May;280(10):2138-49. doi: 10.1111/febs.12149. Epub 2013 Feb 15. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23351020 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Seino S., Bell G. I. (1989) Alternative splicing of human insulin receptor messenger RNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 159, 312–316 - PubMed
-
- Papa V., Gliozzo B., Clark G. M., McGuire W. L., Moore D., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Vigneri R., Goldfine I. D., Pezzino V. (1993) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptors are overexpressed and predict a low risk in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 53, 3736–3740 - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi Y., Flier J. S., Benecke H., Ransil B. J., Moller D. E. (1993) Ligand-binding properties of the two isoforms of the human insulin receptor. Endocrinology 132, 1132–1138 - PubMed
-
- Kosaki A., Webster N. J. (1993) Effect of dexamethasone on the alternative splicing of the insulin receptor mRNA and insulin action in HepG2 hepatoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 21990–21996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

