Structural basis for selective vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) binding to neuropilin-1
- PMID: 22318724
- PMCID: PMC3322888
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.331140
Structural basis for selective vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) binding to neuropilin-1
Abstract
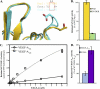
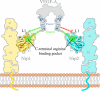
Neuropilin-1 (Nrp1) is an essential receptor for angiogenesis that binds to VEGF-A. Nrp1 binds directly to VEGF-A with high affinity, but the nature of their selective binding has remained unclear. Nrp1 was initially reported to bind to the exon 7-encoded region of VEGF-A and function as an isoform-specific receptor for VEGF-A(164/165). Recent data have implicated exon 8-encoded residues, which are found in all proangiogenic VEGF-A isoforms, in Nrp binding. We have determined the crystal structure of the exon 7/8-encoded VEGF-A heparin binding domain in complex with the Nrp1-b1 domain. This structure clearly demonstrates that residues from both exons 7 and 8 physically contribute to Nrp1 binding. Using an in vitro binding assay, we have determined the relative contributions of exon 7- and 8-encoded residues. We demonstrate that the exon 8-encoded C-terminal arginine is essential for the interaction of VEGF-A with Nrp1 and mediates high affinity Nrp binding. Exon 7-encoded electronegative residues make additional interactions with the L1 loop of Nrp1. Although otherwise conserved, the primary sequences of Nrp1 and Nrp2 differ significantly in this region. We further show that VEGF-A(164) binds 50-fold more strongly to Nrp1 than Nrp2. Direct repulsion between the electronegative exon 7-encoded residues of the heparin binding domain and the electronegative L1 loop found only in Nrp2 is found to significantly contribute to the observed selectivity. The results reveal the basis for the potent and selective binding of VEGF-A(164) to Nrp1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N-terminal modification of VEGF-A C terminus-derived peptides delineates structural features involved in neuropilin-1 binding and functional activity.Chembiochem. 2014 May 26;15(8):1161-70. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201300658. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Chembiochem. 2014. PMID: 24771685
-
Mechanism of selective VEGF-A binding by neuropilin-1 reveals a basis for specific ligand inhibition.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049177. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23145112 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF binding to NRP1 is essential for VEGF stimulation of endothelial cell migration, complex formation between NRP1 and VEGFR2, and signaling via FAK Tyr407 phosphorylation.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Aug 1;22(15):2766-76. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E09-12-1061. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21653826 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF-A121a binding to Neuropilins - A concept revisited.Cell Adh Migr. 2018 May 4;12(3):204-214. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2017.1372878. Epub 2017 Nov 2. Cell Adh Migr. 2018. PMID: 29095088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interaction of Neuropilin-1 and Neuropilin-2 with tyrosine-kinase receptors for VEGF.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;515:81-90. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0119-0_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12613545 Review.
Cited by
-
In silico identification and validation of inhibitors of the interaction between neuropilin receptor 1 and SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Sep 23:2020.09.22.308783. doi: 10.1101/2020.09.22.308783. bioRxiv. 2020. PMID: 32995772 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
In Silico and In Vitro Studies of Alchemilla viridiflora Rothm-Polyphenols' Potential for Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Internalization.Molecules. 2022 Aug 14;27(16):5174. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165174. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014415 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture and hydration of the arginine-binding site of neuropilin-1.FEBS J. 2018 Apr;285(7):1290-1304. doi: 10.1111/febs.14405. Epub 2018 Feb 25. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29430837 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Rho GTPases in VEGF Signaling in Cancer Cells.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2020 Apr 16;2020:2097214. doi: 10.1155/2020/2097214. eCollection 2020. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2020. PMID: 32377503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The carboxyl terminus of VEGF-A is a potential target for anti-angiogenic therapy.Angiogenesis. 2015 Jan;18(1):23-30. doi: 10.1007/s10456-014-9444-3. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Angiogenesis. 2015. PMID: 25274272 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pellet-Many C., Frankel P., Jia H., Zachary I. (2008) Neuropilins: structure, function and role in disease. Biochem. J. 411, 211–226 - PubMed
-
- Kitsukawa T., Shimizu M., Sanbo M., Hirata T., Taniguchi M., Bekku Y., Yagi T., Fujisawa H. (1997) Neuropilin-semaphorin III/D-mediated chemorepulsive signals play a crucial role in peripheral nerve projection in mice. Neuron 19, 995–1005 - PubMed
-
- Grünewald F. S., Prota A. E., Giese A., Ballmer-Hofer K. (2010) Structure-function analysis of VEGF receptor activation and the role of coreceptors in angiogenic signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1804, 567–580 - PubMed
-
- Keyt B. A., Berleau L. T., Nguyen H. V., Chen H., Heinsohn H., Vandlen R., Ferrara N. (1996) The carboxyl-terminal domain(111–165) of vascular endothelial growth factor is critical for its mitogenic potency. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 7788–7795 - PubMed
-
- Houck K. A., Leung D. W., Rowland A. M., Winer J., Ferrara N. (1992) Dual regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor bioavailability by genetic and proteolytic mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 26031–26037 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

