A structure-based mechanism for Arf1-dependent recruitment of coatomer to membranes
- PMID: 22304919
- PMCID: PMC3285272
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.015
A structure-based mechanism for Arf1-dependent recruitment of coatomer to membranes
Abstract
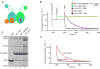
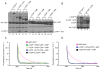
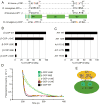
Budding of COPI-coated vesicles from Golgi membranes requires an Arf family G protein and the coatomer complex recruited from cytosol. Arf is also required with coatomer-related clathrin adaptor complexes to bud vesicles from the trans-Golgi network and endosomal compartments. To understand the structural basis for Arf-dependent recruitment of a vesicular coat to the membrane, we determined the structure of Arf1 bound to the γζ-COP subcomplex of coatomer. Structure-guided biochemical analysis reveals that a second Arf1-GTP molecule binds to βδ-COP at a site common to the γ- and β-COP subunits. The Arf1-binding sites on coatomer are spatially related to PtdIns4,5P(2)-binding sites on the endocytic AP2 complex, providing evidence that the orientation of membrane binding is general for this class of vesicular coat proteins. A bivalent GTP-dependent binding mode has implications for the dynamics of coatomer interaction with the Golgi and for the selection of cargo molecules.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
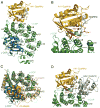

Similar articles
-
Multiple and stepwise interactions between coatomer and ADP-ribosylation factor-1 (Arf1)-GTP.Traffic. 2007 May;8(5):582-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00554.x. Traffic. 2007. PMID: 17451557
-
Regulation of GTP hydrolysis on ADP-ribosylation factor-1 at the Golgi membrane.J Biol Chem. 2001 Dec 21;276(51):47834-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106000200. Epub 2001 Oct 9. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11592960
-
Dissection of COPI and Arf1 dynamics in vivo and role in Golgi membrane transport.Nature. 2002 May 9;417(6885):187-93. doi: 10.1038/417187a. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12000962
-
The role of ADP-ribosylation factor and SAR1 in vesicular trafficking in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jul 1;1664(1):9-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.04.005. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15238254 Review.
-
The structure of COPI vesicles and regulation of vesicle turnover.FEBS Lett. 2023 Mar;597(6):819-835. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14560. Epub 2022 Dec 30. FEBS Lett. 2023. PMID: 36513395 Review.
Cited by
-
BIG1, a brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein modulates ATP-binding cassette transporter A-1 trafficking and function.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Feb;33(2):e31-8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300720. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23220274 Free PMC article.
-
p24 family proteins: key players in the regulation of trafficking along the secretory pathway.Protoplasma. 2016 Jul;253(4):967-85. doi: 10.1007/s00709-015-0858-6. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Protoplasma. 2016. PMID: 26224213 Review.
-
Arf6 regulation of Gyrating-clathrin.Traffic. 2013 Jan;14(1):97-106. doi: 10.1111/tra.12014. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Traffic. 2013. PMID: 22998223 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics of Arf1 inactivation regulates Golgi organisation and function in non-adherent fibroblasts.Biol Open. 2023 Apr 15;12(4):bio059669. doi: 10.1242/bio.059669. Epub 2023 May 4. Biol Open. 2023. PMID: 36946871 Free PMC article.
-
A Bayesian semi-parametric model for thermal proteome profiling.Commun Biol. 2021 Jun 29;4(1):810. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02306-8. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34188175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmadian MR, Hoffman U, Goody RS, Wittinghofer A. Individual rate constants for the interaction of Ras proteins with GTPase-activating proteins determined by fluorescence spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1997;36:4535–4541. - PubMed
-
- Amor JC, Harrison DH, Kahn RA, Ringe D. Structure of the human ADP-ribosylation factor 1 complexed with GDP. Nature. 1994;372:704–708. - PubMed
-
- Antonny B, Beraud-Dufour S, Chardin P, Chabre M. N-terminal hydrophobic residues of the G-protein ADP-ribosylation factor-1 insert into membrane phospholipids upon GDP to GTP exchange. Biochemistry. 1997;36:4675–4684. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by Sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;77:895–907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

