Analysis of beta-cell gene expression reveals inflammatory signaling and evidence of dedifferentiation following human islet isolation and culture
- PMID: 22299040
- PMCID: PMC3267725
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030415
Analysis of beta-cell gene expression reveals inflammatory signaling and evidence of dedifferentiation following human islet isolation and culture
Abstract
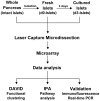
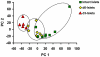
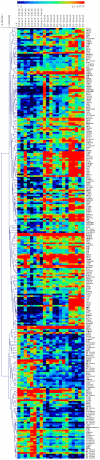
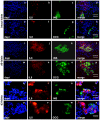
The stresses encountered during islet isolation and culture may have deleterious effects on beta-cell physiology. However, the biological response of human islet cells to isolation remains poorly characterized. A better understanding of the network of signaling pathways induced by islet isolation and culturing may lead to strategies aimed at improving islet graft survival and function. Laser capture microdissection (LCM) was used to extract beta-cell RNA from 1) intact pancreatic islets, 2) freshly isolated islets, 3) islets cultured for 3 days, and changes in gene expression were examined by microarray analysis. We identified a strong inflammatory response induced by islet isolation that continues during in-vitro culture manifested by upregulation of several cytokines and cytokine-receptors. The most highly upregulated gene, interleukin-8 (IL-8), was induced by 3.6-fold following islet isolation and 56-fold after 3 days in culture. Immunofluorescence studies showed that the majority of IL-8 was produced by beta-cells themselves. We also observed that several pancreas-specific transcription factors were down-regulated in cultured islets. Concordantly, several pancreatic progenitor cell-specific transcription factors like SOX4, SOX9, and ID2 were upregulated in cultured islets, suggesting progressive transformation of mature beta-cell phenotype toward an immature endocrine cell phenotype. Our findings suggest islet isolation and culture induces an inflammatory response and loss of the mature endocrine cell phenotype. A better understanding of the signals required to maintain a mature beta-cell phenotype may help improve the efficacy of islet transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in gene expression in beta cells after islet isolation and transplantation using laser-capture microdissection.Diabetologia. 2007 Feb;50(2):334-42. doi: 10.1007/s00125-006-0536-5. Epub 2006 Dec 16. Diabetologia. 2007. PMID: 17180350
-
Single-cell transcriptomics of human islet ontogeny defines the molecular basis of β-cell dedifferentiation in T2D.Mol Metab. 2020 Dec;42:101057. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101057. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32739450 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Expression Analysis of In Vitro Dedifferentiated Human Pancreatic Islet Cells Reveals the Activation of the Pluripotency-Related MicroRNA Cluster miR-302s.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 12;19(4):1170. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041170. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29649109 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-induced adaptive islet cell identity changes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016 Sep;18 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):87-96. doi: 10.1111/dom.12726. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2016. PMID: 27615136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and functional profiling of human islets: from heterogeneity to human phenotypes.Diabetologia. 2020 Oct;63(10):2095-2101. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05159-8. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 32894320 Review.
Cited by
-
Unstable Expression of Commonly Used Reference Genes in Rat Pancreatic Islets Early after Isolation Affects Results of Gene Expression Studies.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 1;11(4):e0152664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152664. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27035827 Free PMC article.
-
Islet neogenesis associated protein (INGAP) protects pancreatic β cells from IL-1β and IFNγ-induced apoptosis.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Mar 17;7(1):56. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00441-z. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 33731692 Free PMC article.
-
Perlecan: An Islet Basement Membrane Protein with Protective Anti-Inflammatory Characteristics.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Aug 13;11(8):828. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11080828. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199786 Free PMC article.
-
Systems biology of the IMIDIA biobank from organ donors and pancreatectomised patients defines a novel transcriptomic signature of islets from individuals with type 2 diabetes.Diabetologia. 2018 Mar;61(3):641-657. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4500-3. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29185012 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokines as Drivers of the Autoimmune Destruction in Type 1 Diabetes: Opportunity for Therapeutic Intervention in Consideration of an Optimal Treatment Schedule.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Oct 19;11:591083. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.591083. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33193102 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, et al. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1318–1330. - PubMed
-
- Paraskevas S, Maysinger D, Wang R, Duguid TP, Rosenberg L. Cell loss in isolated human islets occurs by apoptosis. Pancreas. 2000;20:270–276. - PubMed
-
- Russ HA, Bar Y, Ravassard P, Efrat S. In vitro proliferation of cells derived from adult human beta-cells revealed by cell-lineage tracing. Diabetes. 2008;57:1575–1583. - PubMed
-
- Paraskevas S, Aikin R, Maysinger D, Lakey JR, Cavanagh TJ, et al. Activation and expression of ERK, JNK, and p38 MAP-kinases in isolated islets of Langerhans: implications for cultured islet survival. FEBS Lett. 1999;455:203–208. - PubMed
-
- Marzorati S, Antonioli B, Nano R, Maffi P, Piemonti L, et al. Culture medium modulates proinflammatory conditions of human pancreatic islets before transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2006;6:2791–2795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

