Comparing statistical methods for constructing large scale gene networks
- PMID: 22272232
- PMCID: PMC3260142
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029348
Comparing statistical methods for constructing large scale gene networks
Abstract
The gene regulatory network (GRN) reveals the regulatory relationships among genes and can provide a systematic understanding of molecular mechanisms underlying biological processes. The importance of computer simulations in understanding cellular processes is now widely accepted; a variety of algorithms have been developed to study these biological networks. The goal of this study is to provide a comprehensive evaluation and a practical guide to aid in choosing statistical methods for constructing large scale GRNs. Using both simulation studies and a real application in E. coli data, we compare different methods in terms of sensitivity and specificity in identifying the true connections and the hub genes, the ease of use, and computational speed. Our results show that these algorithms performed reasonably well, and each method has its own advantages: (1) GeneNet, WGCNA (Weighted Correlation Network Analysis), and ARACNE (Algorithm for the Reconstruction of Accurate Cellular Networks) performed well in constructing the global network structure; (2) GeneNet and SPACE (Sparse PArtial Correlation Estimation) performed well in identifying a few connections with high specificity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

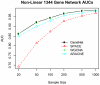
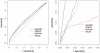
 0.005 for various methods.
0.005 for various methods.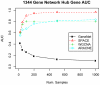
Similar articles
-
MICRAT: a novel algorithm for inferring gene regulatory networks using time series gene expression data.BMC Syst Biol. 2018 Dec 14;12(Suppl 7):115. doi: 10.1186/s12918-018-0635-1. BMC Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 30547796 Free PMC article.
-
A Sparse Reconstruction Approach for Identifying Gene Regulatory Networks Using Steady-State Experiment Data.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0130979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130979. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26207991 Free PMC article.
-
ANCA: Alignment-Based Network Construction Algorithm.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2021 Mar-Apr;18(2):512-524. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2019.2923620. Epub 2021 Apr 8. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 31226082
-
Computational reconstruction of protein-protein interaction networks: algorithms and issues.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;541:89-100. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-243-4_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19381528 Review.
-
Computational prediction of gene regulatory networks in plant growth and development.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2019 Feb;47:96-105. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2018.10.005. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 30445315 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of co-expression measures: mutual information, correlation, and model based indices.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012 Dec 9;13:328. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-328. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23217028 Free PMC article.
-
Network analysis of human muscle adaptation to aging and contraction.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jan 7;12(1):740-755. doi: 10.18632/aging.102653. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 31910159 Free PMC article.
-
CCor: A whole genome network-based similarity measure between two genes.Biometrics. 2016 Dec;72(4):1216-1225. doi: 10.1111/biom.12508. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Biometrics. 2016. PMID: 26953524 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of Gene Networks and Their Application to Lung Adenocarcinoma Studies.Cancer Inform. 2017 Feb 23;16:1176935117690778. doi: 10.1177/1176935117690778. eCollection 2017. Cancer Inform. 2017. PMID: 28469387 Free PMC article.
-
Differential network analysis reveals genetic effects on catalepsy modules.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58951. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058951. Epub 2013 Mar 21. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman N. Inferring cellular networks using probabilistic graphical models. Science. 2004;303:799–805. - PubMed
-
- Ihmels J, Friedlander G, Bergmann S, Sarig O, Ziv Y, et al. Revealing modular organization in the yeast transcriptional network. Nat Genet. 2002;31:370–7. - PubMed
-
- Lee I, Date SV, Adai AT, Marcotte EM. A probabilistic functional network of yeast genes. Science. 2004;306:1555–8. - PubMed
-
- Sachs K, Perez O, Pe'er D, Lauffenburger DA, Nolan GP. Causal protein-signaling networks derived from multiparameter single-cell data. Science. 2005;308:523–9. - PubMed
-
- Segal E, Shapira M, Regev A, Pe'er D, Botstein D, et al. Module networks: identifying regulatory modules and their condition-specific regulators from gene expression data. Nat Genet. 2003;34:166–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

