Regulation of Rev1 by the Fanconi anemia core complex
- PMID: 22266823
- PMCID: PMC3280818
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2222
Regulation of Rev1 by the Fanconi anemia core complex
Abstract
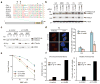
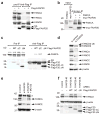
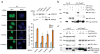
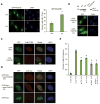
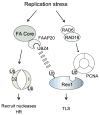
The 15 known Fanconi anemia proteins cooperate in a pathway that regulates DNA interstrand cross-link repair. Recent studies indicate that the Fanconi anemia pathway also controls Rev1-mediated translesion DNA synthesis (TLS). We identified Fanconi anemia-associated protein (FAAP20), an integral subunit of the multisubunit Fanconi anemia core complex. FAAP20 binds to FANCA subunit and is required for stability of the complex and monoubiquitination of FANCD2. FAAP20 contains a ubiquitin-binding zinc finger 4 domain and binds to the monoubiquitinated form of Rev1. FAAP20 binding stabilizes Rev1 nuclear foci and promotes interaction of the Fanconi anemia core with PCNA-Rev1 DNA damage bypass complexes. FAAP20 therefore provides a critical link between the Fanconi anemia pathway and TLS polymerase activity. We propose that the Fanconi anemia core complex regulates cross-link repair by channeling lesions to damage bypass pathways and preventing large DNA insertions and deletions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acetylation modulates the Fanconi anemia pathway by protecting FAAP20 from ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation.J Biol Chem. 2020 Oct 2;295(40):13887-13901. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015288. Epub 2020 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32763975 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysical characterization of the interaction between FAAP20-UBZ4 domain and Rev1-BRCT domain.FEBS Lett. 2015 Oct 7;589(20 Pt B):3037-43. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.08.021. Epub 2015 Aug 28. FEBS Lett. 2015. PMID: 26318859
-
Fanconi anemia (FA) binding protein FAAP20 stabilizes FA complementation group A (FANCA) and participates in interstrand cross-link repair.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Mar 20;109(12):4491-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1118720109. Epub 2012 Mar 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22396592 Free PMC article.
-
The Fanconi anemia ID2 complex: dueling saxes at the crossroads.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(19):2999-3015. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.956475. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25486561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A defined role for multiple Fanconi anemia gene products in DNA-damage-associated ubiquitination.Exp Hematol. 2017 Jun;50:27-32. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Exp Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28315701 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetylation modulates the Fanconi anemia pathway by protecting FAAP20 from ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation.J Biol Chem. 2020 Oct 2;295(40):13887-13901. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015288. Epub 2020 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32763975 Free PMC article.
-
Bypass of DNA interstrand crosslinks by a Rev1-DNA polymerase ζ complex.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Sep 4;48(15):8461-8473. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa580. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32633759 Free PMC article.
-
REV7 is required for anaphase-promoting complex-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of translesion DNA polymerase REV1.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jan 15;12(2):365-78. doi: 10.4161/cc.23214. Epub 2012 Jan 15. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23287467 Free PMC article.
-
Using ultra-sensitive next generation sequencing to dissect DNA damage-induced mutagenesis.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 28;6:25310. doi: 10.1038/srep25310. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27122023 Free PMC article.
-
The structural basis of XRCC1-mediated DNA repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 Jun;30:90-103. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Feb 16. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25795425 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

