Using formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE) to isolate active regulatory DNA
- PMID: 22262007
- PMCID: PMC3784247
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2011.444
Using formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE) to isolate active regulatory DNA
Erratum in
- Nat Protoc. 2014 Feb;9(2):501-3
Abstract
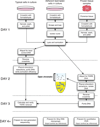
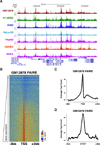
Eviction or destabilization of nucleosomes from chromatin is a hallmark of functional regulatory elements in eukaryotic genomes. Historically identified by nuclease hypersensitivity, these regulatory elements are typically bound by transcription factors or other regulatory proteins. FAIRE (formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements) is an alternative approach to identify these genomic regions and has proven successful in a multitude of eukaryotic cell and tissue types. Cells or dissociated tissues are cross-linked briefly with formaldehyde, lysed and sonicated. Sheared chromatin is subjected to phenol/chloroform extraction and the isolated DNA, typically encompassing 1-3% of the human genome, is purified. We provide guidelines for quantitative analysis by PCR, microarrays or next-generation sequencing. Regulatory elements enriched by FAIRE have high concordance with those identified by nuclease hypersensitivity or chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and the entire procedure can be completed in 3 d. FAIRE has low technical variability, which allows its usage in large-scale studies of chromatin from normal or diseased tissues.
Figures

Similar articles
-
FAIRE (Formaldehyde-Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements) isolates active regulatory elements from human chromatin.Genome Res. 2007 Jun;17(6):877-85. doi: 10.1101/gr.5533506. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Genome Res. 2007. PMID: 17179217 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of active regulatory elements from eukaryotic chromatin using FAIRE (Formaldehyde Assisted Isolation of Regulatory Elements).Methods. 2009 Jul;48(3):233-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2009.03.003. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Methods. 2009. PMID: 19303047 Free PMC article.
-
A detailed protocol for formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE).Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2013;Chapter 21:Unit21.26. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb2126s102. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23547014
-
Formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009 Nov-Dec;1(3):400-406. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.36. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2009. PMID: 20046543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serial analysis of binding elements for transcription factors.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;567:113-32. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-414-2_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19588089 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of new Anopheles gambiae transcriptional enhancers using a cross-species prediction approach.Insect Mol Biol. 2021 Aug;30(4):410-419. doi: 10.1111/imb.12705. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Insect Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33866636 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA ChRO1 facilitates ATRX/DAXX-dependent H3.3 deposition for transcription-associated heterochromatin reorganization.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Dec 14;46(22):11759-11775. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky923. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30335163 Free PMC article.
-
Transposition of native chromatin for fast and sensitive epigenomic profiling of open chromatin, DNA-binding proteins and nucleosome position.Nat Methods. 2013 Dec;10(12):1213-8. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2688. Epub 2013 Oct 6. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 24097267 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Coding Variants in Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Potential for Personalized Medicine.Noncoding RNA. 2021 Aug 2;7(3):47. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7030047. Noncoding RNA. 2021. PMID: 34449663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Su(Hw) primes 66D and 7F Drosophila chorion genes loci for amplification through chromatin decondensation.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 20;11(1):16963. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96488-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34417521 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

