Neuroinflammation: a common pathway in CNS diseases as mediated at the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 22248728
- PMCID: PMC3707010
- DOI: 10.1159/000330247
Neuroinflammation: a common pathway in CNS diseases as mediated at the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
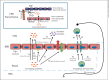
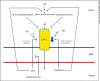
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is not simply a physical barrier but a regulatory interface between the central nervous system (CNS) and immune system. The BBB both affects and is affected by the immune system and connects at many levels with the CNS, including the following: (1) the BBB transports cytokines and secretes various substances with neuroinflammatory properties; (2) transporters are altered in disease states including traumatic injury, Alzheimer's disease and inflammatory processes; (3) cytokines and other immune secretions from the cells comprising the BBB are both constitutive and inducible; (4) immune cells are transported across the BBB by the highly regulated process termed diapedesis, which involves communication and interactions between the brain endothelial cells and the immune cells; (5) the neuroimmune system has various effects on the BBB, including modulation of important transport systems and in extreme pathological conditions even disruption of the BBB, and (6) the brain-to-blood efflux transporter P-glycoprotein is altered in inflammatory conditions, thus affecting drug delivery to the brain. In summary, the BBB is an interactive interface that regulates and defines many of the ways that the CNS and the immune system communicate with one another.
Copyright © 2012 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The blood-brain barrier in neuroimmunology: Tales of separation and assimilation.Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Feb;44:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.08.007. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Brain Behav Immun. 2015. PMID: 25172555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroimmune Axes of the Blood-Brain Barriers and Blood-Brain Interfaces: Bases for Physiological Regulation, Disease States, and Pharmacological Interventions.Pharmacol Rev. 2018 Apr;70(2):278-314. doi: 10.1124/pr.117.014647. Pharmacol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29496890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The blood-brain barrier in psychoneuroimmunology.Neurol Clin. 2006 Aug;24(3):413-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2006.03.009. Neurol Clin. 2006. PMID: 16877115 Review.
-
The blood-brain barrier in psychoneuroimmunology.Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009 May;29(2):223-8. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2009.02.001. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009. PMID: 19389578
-
In vitro modeling of blood-brain barrier and interface functions in neuroimmune communication.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020 Mar 30;17(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12987-020-00187-3. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020. PMID: 32228633 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transitory loss of glia and the subsequent modulation in inflammatory cytokines/chemokines regulate paracellular claudin-5 expression in endothelial cells.J Neuroimmunol. 2015 Jul 15;284:57-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 May 13. J Neuroimmunol. 2015. PMID: 26025059 Free PMC article.
-
An Injury-like Signature of the Extracellular Glioma Metabolome.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 30;16(15):2705. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152705. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123433 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional and Nanotechnological Modulators of Microglia.Front Immunol. 2016 Jul 15;7:270. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00270. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27471505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation of cytokines, BDNF levels, and memory function in patients with opioid use disorder undergoing methadone maintenance treatment.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018 Oct 1;191:6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2018.06.024. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2018. PMID: 30071446 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing blood-brain barrier perturbations after exposure to human triglyceride-rich lipoprotein lipolysis products using MRI in a rat model.Magn Reson Med. 2016 Oct;76(4):1246-51. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25985. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Magn Reson Med. 2016. PMID: 26485349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watkins LR, Maier SF, Goehler LE. Cytokine-to-brain communication: a review & analysis of alternative mechanisms. Life Sci. 1995;57:1011–1026. - PubMed
-
- Avison MJ, Nath A, Greene-Avison R, Schmitt FA, Bales RA, Ethisham A, Greenberg RN, Berger JR. Inflammatory changes and breakdown of microvascular integrity in early human immunodeficiency virus dementia. J Neurovirol. 2004;10:223–232. - PubMed
-
- Chou S, Dix RD. Viral infections and the blood-brain barrier. In: Neuwelt EA, editor. Implications of the Blood-Brain Barrier and Its Manipulation, vol 2: Clinical Aspects. New York: Plenum; 1989. pp. 449–468.
-
- Rapoport SI. Pathological Alterations of the Blood-Brain Barrier; Blood-Brain Barrier in Physiology and Medicine. New York: Raven; 1976. pp. 129–152.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

