LPS induced inflammatory responses in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells is mediated through NOX4 and Giα dependent PI-3kinase signalling
- PMID: 22239975
- PMCID: PMC3293082
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-9-1
LPS induced inflammatory responses in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells is mediated through NOX4 and Giα dependent PI-3kinase signalling
Abstract
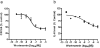
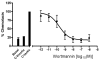
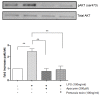
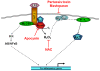
COPD is a disease of innate immunity and bacterial infections are a dominant cause of exacerbations in the later stages resulting in poor health and high mortality. The pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP) lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is sensed by immune cells through activation of the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). This leads to the activation of NADPH oxidase (NOX) and NF-κB which together drive COPD inflammation. In this study we show in human PBMCs that LPS stimulated proinflammatory cytokine release (CXCL8 and IL6) was inhibited by approximately 50% by the broad specificity phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor, wortmannin. Our results also demonstrate that activation of PI3K following LPS stimulation is mediated by a NOX4 dependent mechanism releasing endogenous H2O2, as the NOX4 inhibitor apocynin blocked LPS induced AKT phosphorylation. Moreover, LPS-induced PI3K activation was inhibited by the anti-oxidant N-acetylcysteine in a concentration dependent manner (IC50 ~100 μM). In addition, our data demonstrated that inhibition of small G proteins, by pre-treatment with pertussis toxin, inhibited LPS-induced AKT phosphorylation. Furthermore, the G-protein inhibitors pertussis toxin and mastoparan both inhibited LPS-induced CXCL8 and IL-6 release by approximately 50%. Together, these data indicate there is a mechanism in human PBMCs where TLR4 activation by LPS leads to ROS generation through NOX4 and activation of the PI3K pathway. This effect is apparently mediated through small G proteins facilitating the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Figures
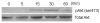
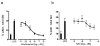
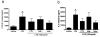
Similar articles
-
Lipopolysaccharide induces ICAM-1 expression via a c-Src/NADPH oxidase/ROS-dependent NF-κB pathway in human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Apr 1;310(7):L639-57. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00109.2014. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26747779
-
SAA1 increases NOX4/ROS production to promote LPS-induced inflammation in vascular smooth muscle cells through activating p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Jun 19;20(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12860-019-0197-0. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31216990 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide enhances Wnt5a expression through toll-like receptor 4, myeloid differentiating factor 88, phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase/AKT and nuclear factor kappa B pathways in human dental pulp stem cells.J Endod. 2014 Jan;40(1):69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2013.09.011. Epub 2013 Oct 22. J Endod. 2014. PMID: 24331994
-
Role of the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase-Akt pathway in the regulation of IL-10 and IL-12 by Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide.J Immunol. 2003 Jul 15;171(2):717-25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.2.717. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12847238
-
Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)/Opioid Receptor Pathway Crosstalk and Impact on Opioid Analgesia, Immune Function, and Gastrointestinal Motility.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 8;11:1455. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01455. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32733481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Time-Resolved and Comprehensive Analysis of Surface Glycoproteins Reveals Distinct Responses of Monocytes and Macrophages to Bacterial Infection.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 May 10;60(20):11494-11503. doi: 10.1002/anie.202102692. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 33684247 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations and Prediction of Functional Profiles of Gut Microbiota After Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Iranian Recurrent Clostridioides difficile Infection with Underlying Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Pilot Study.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Jan 6;15:105-116. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S338212. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35023946 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and Immune Functions of Punicalagin.Nutrients. 2021 Jun 23;13(7):2150. doi: 10.3390/nu13072150. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34201484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Oxyresveratrol Tetraacetate, an Ester Prodrug of Oxyresveratrol, on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophage Cells.Molecules. 2022 Jun 18;27(12):3922. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123922. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35745046 Free PMC article.
-
Capsaicin Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Barrier Dysfunction in Intestinal Porcine Epithelial Cell Line-J2.Front Physiol. 2021 Sep 24;12:715469. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.715469. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34630139 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

