Epigenetic changes of CXCR4 and its ligand CXCL12 as prognostic factors for sporadic breast cancer
- PMID: 22220212
- PMCID: PMC3248418
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029461
Epigenetic changes of CXCR4 and its ligand CXCL12 as prognostic factors for sporadic breast cancer
Abstract
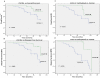
Chemokines and their receptors are involved in the development and cancer progression. The chemokine CXCL12 interacts with its receptor, CXCR4, to promote cellular adhesion, survival, proliferation and migration. The CXCR4 gene is upregulated in several types of cancers, including skin, lung, pancreas, brain and breast tumors. In pancreatic cancer and melanoma, CXCR4 expression is regulated by DNA methylation within its promoter region. In this study we examined the role of cytosine methylation in the regulation of CXCR4 expression in breast cancer cell lines and also correlated the methylation pattern with the clinicopathological aspects of sixty-nine primary breast tumors from a cohort of Brazilian women. RT-PCR showed that the PMC-42, MCF7 and MDA-MB-436 breast tumor cell lines expressed high levels of CXCR4. Conversely, the MDA-MB-435 cell line only expressed CXCR4 after treatment with 5-Aza-CdR, which suggests that CXCR4 expression is regulated by DNA methylation. To confirm this hypothesis, a 184 bp fragment of the CXCR4 gene promoter region was cloned after sodium bisulfite DNA treatment. Sequencing data showed that cell lines that expressed CXCR4 had only 15% of methylated CpG dinucleotides, while the cell line that not have CXCR4 expression, had a high density of methylation (91%). Loss of DNA methylation in the CXCR4 promoter was detected in 67% of the breast cancer analyzed. The absence of CXCR4 methylation was associated with the tumor stage, size, histological grade, lymph node status, ESR1 methylation and CXCL12 methylation, metastasis and patient death. Kaplan-Meier curves demonstrated that patients with an unmethylated CXCR4 promoter had a poorer overall survival and disease-free survival. Furthermore, patients with both CXCL12 methylation and unmethylated CXCR4 had a shorter overall survival and disease-free survival. These findings suggest that the DNA methylation status of both CXCR4 and CXCL12 genes could be used as a biomarker for prognosis in breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Simultaneous CXCL12 and ESR1 CpG island hypermethylation correlates with poor prognosis in sporadic breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2010 Jan 28;10:23. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-23. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20109227 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of CXCL12 mRNA expression by promoter hypermethylation and its association with metastatic progression in human breast carcinomas.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009 Jan;135(1):91-102. doi: 10.1007/s00432-008-0435-x. Epub 2008 Aug 1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 18670789
-
Prognostic significance of CXCL12, CXCR4, and CXCR7 in patients with breast cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Oct 1;8(10):13217-24. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26722521 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of CXCR4 signaling in cancer pathogenesis and progression.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Nov;86(Pt 2):697-708. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.03.019. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 35346802 Review.
-
Demystifying the CXCR4 conundrum in cancer biology: Beyond the surface signaling paradigm.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022 Sep;1877(5):188790. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2022.188790. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36058380 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-induced cancer stemness acquisition is associated with CXCR4 activation by its aberrant promoter demethylation.BMC Cancer. 2019 Feb 13;19(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5360-7. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30760238 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in breast cancer metastasis.Am J Cancer Res. 2013;3(1):46-57. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Am J Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23359227 Free PMC article.
-
Why the stroma matters in breast cancer: insights into breast cancer patient outcomes through the examination of stromal biomarkers.Cell Adh Migr. 2012 May-Jun;6(3):249-60. doi: 10.4161/cam.20567. Epub 2012 May 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 22568982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic mechanisms and implications in tendon inflammation (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2019 Jan;43(1):3-14. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3961. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30387824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Rewiring of Metastatic Cancer to the Brain: Focus on Lung and Colon Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Apr 4;15(7):2145. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072145. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer Statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 2010 - PubMed
-
- INCA. Incidência do câncer no Brasil. 2012. Estimativa 2012. 100.
-
- Weigelt B, Peterse JL, van 't Veer LJ. Breast cancer metastasis: markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:591–602. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

