Inhibition of the Nedd8 system sensitizes cells to DNA interstrand cross-linking agents
- PMID: 22219386
- PMCID: PMC3307881
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0497
Inhibition of the Nedd8 system sensitizes cells to DNA interstrand cross-linking agents
Abstract
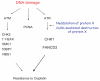
The Fanconi anemia pathway is required for repair of DNA interstrand cross-links (ICL). Fanconi anemia pathway-deficient cells are hypersensitive to DNA ICL-inducing drugs such as cisplatin. Conversely, hyperactivation of the Fanconi anemia pathway is a mechanism that may underlie cellular resistance to DNA ICL agents. Modulating FANCD2 monoubiquitination, a key step in the Fanconi anemia pathway, may be an effective therapeutic approach to conferring cellular sensitivity to ICL agents. Here, we show that inhibition of the Nedd8 conjugation system increases cellular sensitivity to DNA ICL-inducing agents. Mechanistically, the Nedd8 inhibition, either by siRNA-mediated knockdown of Nedd8-conjugating enzymes or treatment with a Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924, suppressed DNA damage-induced FANCD2 monoubiquitination and CHK1 phosphorylation. Our data indicate that inhibition of the Fanconi anemia pathway is largely responsible for the heightened cellular sensitivity to DNA ICLs upon Nedd8 inhibition. These results suggest that a combination of Nedd8 inhibition with ICL-inducing agents may be an effective strategy for sensitizing a subset of drug-resistant cancer cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loss of CHK1 function impedes DNA damage-induced FANCD2 monoubiquitination but normalizes the abnormal G2 arrest in Fanconi anemia.Hum Mol Genet. 2008 Mar 1;17(5):679-89. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm340. Epub 2007 Nov 20. Hum Mol Genet. 2008. PMID: 18029388
-
Promyelocytic Leukemia Proteins Regulate Fanconi Anemia Gene Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 21;22(15):7782. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157782. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360546 Free PMC article.
-
Acquisition of Relative Interstrand Crosslinker Resistance and PARP Inhibitor Sensitivity in Fanconi Anemia Head and Neck Cancers.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Apr 15;21(8):1962-72. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2616. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25609062 Free PMC article.
-
DNA interstrand cross-link repair: understanding role of Fanconi anemia pathway and therapeutic implications.Eur J Haematol. 2013 Nov;91(5):381-93. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12169. Epub 2013 Aug 17. Eur J Haematol. 2013. PMID: 23859405 Review.
-
Beyond interstrand crosslinks repair: contribution of FANCD2 and other Fanconi Anemia proteins to the replication of DNA.Mutat Res. 2018 Mar;808:83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Mutat Res. 2018. PMID: 29031493 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploiting replicative stress to treat cancer.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015 Jun;14(6):405-23. doi: 10.1038/nrd4553. Epub 2015 May 8. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2015. PMID: 25953507 Review.
-
Targeting cullin-RING ligases for cancer treatment: rationales, advances and therapeutic implications.Cytotechnology. 2016 Jan;68(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s10616-015-9870-0. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Cytotechnology. 2016. PMID: 25899169 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of glioblastoma by targeting the overactivated protein neddylation pathway.Neuro Oncol. 2015 Oct;17(10):1333-43. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov066. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Neuro Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25904638 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted CUL4A inhibition synergizes with cisplatin to yield long-term survival in models of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through a DDB2-mediated mechanism.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Apr 15;13(4):350. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04798-6. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35428778 Free PMC article.
-
CRL4 ubiquitin ligase stimulates Fanconi anemia pathway-induced single-stranded DNA-RPA signaling.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 5;19(1):1042. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6305-x. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31690264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Helleday T, Petermann E, Lundin C, Hodgson B, Sharma RA. DNA repair pathways as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:193–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

