Milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 is decreased in intestinal epithelium of ulcerative colitis patients and thereby causes increased apoptosis and impaired wound healing
- PMID: 22204000
- PMCID: PMC3356429
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00369
Milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 is decreased in intestinal epithelium of ulcerative colitis patients and thereby causes increased apoptosis and impaired wound healing
Abstract
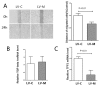
Milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 (MFG-E8) plays an important role in maintaining intestinal barrier homeostasis and accelerating intestinal restitution. However, studies of MFG-E8 expression in humans with ulcerative colitis are lacking. We examined MFG-E8 expression in colonic mucosal biopsies from ulcerative colitis patients and healthy controls (n = 26 each) by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR), Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry. MFG-E8 mRNA and protein expression was lower in ulcerative colitis patients than in controls. MFG-E8 expression was inversely correlated with mucosal inflammatory activity and clinical disease activity in patients. MFG-E8 was present in human intestinal epithelial cells both in vivo and in vitro. Apoptosis induction was also detected in the intestinal epithelium of ulcerative colitis patients by terminal-deoxynucleoitidyl transferase mediated nick-end labeling assay. We used lentiviral vectors encoding human MFG-E8 targeting short hairpin RNA to obtain MFG-E8 knockdown intestinal epithelia cell clones. MFG-E8 knockdown could promote apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cell lines, accompanied by a decrease in level of the antiapoptotic protein B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) and induction of the proapoptotic protein BCL2-associated protein X (BAX). The addition of recombinant human MFG-E8 led to decreased BAX and cleaved caspase-3 levels and induction of BCL-2 level in intestinal epithelia cells. MFG-E8 knockdown also attenuated wound healing on scratch assay of intestinal epithelial cells. The mRNA level of intestinal trefoid factor 3, a pivotal factor in intestinal epithelial cell migration and restitution, was downregulated with MFG-E8 knockdown. In conclusion, we demonstrated that decreased colonic MFG-E8 expression in patients with ulcerative colitis may be associated with mucosal inflammatory activity and clinical disease activity through basal cell apoptosis and preventing tissue healing in the pathogenesis of ulcerative colitis.
Figures
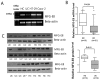
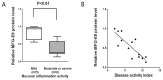
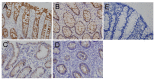
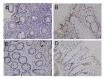
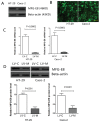
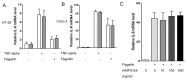
 , LV-M.
, LV-M.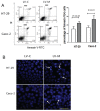
 , LV-M.
, LV-M.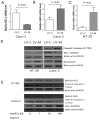
Similar articles
-
Role of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 in colonic inflammation and carcinogenesis.J Gastroenterol. 2015 Aug;50(8):862-75. doi: 10.1007/s00535-014-1036-x. Epub 2015 Jan 18. J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25596854
-
Milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 is a critical protein for healing of dextran sodium sulfate-induced acute colitis in mice.Mol Med. 2011 May-Jun;17(5-6):502-7. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2010.00074. Epub 2011 Feb 4. Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21308148 Free PMC article.
-
Milk fat globule-EGF factor 8/lactadherin plays a crucial role in maintenance and repair of murine intestinal epithelium.J Clin Invest. 2007 Dec;117(12):3673-83. doi: 10.1172/JCI31841. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 18008006 Free PMC article.
-
Milk fat-globule epidermal growth factor 8: A potential Regulator of Cutaneous Wound Healing.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Sep;49(9):8883-8893. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07365-6. Epub 2022 May 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35581508 Review.
-
SED1/MFG-E8: a bi-motif protein that orchestrates diverse cellular interactions.J Cell Biochem. 2009 Apr 15;106(6):957-66. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22076. J Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19204935 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ULK1 and ULK2 are less redundant than previously thought: computational analysis uncovers distinct regulation and functions of these autophagy induction proteins.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 2;10(1):10940. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67780-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32616830 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Repression of MFG-E8 Causes Disturbance in the Homeostasis of Cell Cycle Through DOCK/ZP4/STAT Signaling in Buffalo Mammary Epithelial Cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 1;9:568660. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.568660. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869165 Free PMC article.
-
Role of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 in colonic inflammation and carcinogenesis.J Gastroenterol. 2015 Aug;50(8):862-75. doi: 10.1007/s00535-014-1036-x. Epub 2015 Jan 18. J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25596854
-
Hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus stimulation reduces intestinal injury in rats with ulcerative colitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Apr 14;22(14):3769-76. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3769. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27076761 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour-suppressive function of SIRT4 in human colorectal cancer.Br J Cancer. 2015 Jul 28;113(3):492-9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.226. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26086877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xavier RJ, Podolsky DK. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2007;448:427–34. - PubMed
-
- Podolsky DK. Inflammatory bowel disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:417–29. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda R, et al. Quantitive cytokine mRNA expression profiles in the colonic mucosa of patients with steroid naive ulcerative colitis during active and quiescent disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009;15:328–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

