The internal region leucine-rich repeat 6 of decorin interacts with low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1, modulates transforming growth factor (TGF)-β-dependent signaling, and inhibits TGF-β-dependent fibrotic response in skeletal muscles
- PMID: 22203668
- PMCID: PMC3307262
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.312488
The internal region leucine-rich repeat 6 of decorin interacts with low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1, modulates transforming growth factor (TGF)-β-dependent signaling, and inhibits TGF-β-dependent fibrotic response in skeletal muscles
Abstract
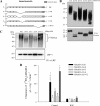
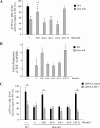
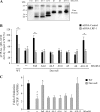
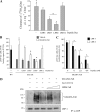
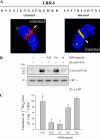
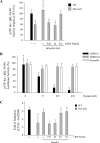
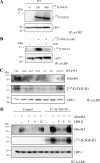
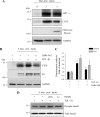
Decorin is a small proteoglycan, composed of 12 leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) that modulates the activity of transforming growth factor type β (TGF-β) and other growth factors, and thereby influences proliferation and differentiation in a wide array of physiological and pathological processes, such as fibrosis, in several tissues and organs. Previously we described two novel modulators of the TGF-β-dependent signaling pathway: LDL receptor-related protein (LRP-1) and decorin. Here we have determined the regions in decorin that are responsible for interaction with LRP-1 and are involved in TGF-β-dependent binding and signaling. Specifically, we used decorin deletion mutants, as well as peptides derived from internal LRR regions, to determine the LRRs responsible for these decorin functions. Our results indicate that LRR6 and LRR5 participate in the interaction with LRP-1 and TGF-β as well as in its dependent signaling. Furthermore, the internal region (LRR6i), composed of 11 amino acids, is responsible for decorin binding to LRP-1 and subsequent TGF-β-dependent signaling. Furthermore, using an in vivo approach, we also demonstrate that the LRR6 region of decorin can inhibit TGF-β mediated action in response to skeletal muscle injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein functions as an endocytic receptor for decorin.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 20;281(42):31562-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602919200. Epub 2006 Aug 25. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16936287
-
A novel modulatory mechanism of transforming growth factor-beta signaling through decorin and LRP-1.J Biol Chem. 2007 Jun 29;282(26):18842-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M700243200. Epub 2007 May 7. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17485468
-
Antisense inhibition of decorin expression in myoblasts decreases cell responsiveness to transforming growth factor beta and accelerates skeletal muscle differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2001 Feb 2;276(5):3589-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004602200. Epub 2000 Nov 8. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11071883
-
Decorin-TGFβ axis in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis.J Histochem Cytochem. 2012 Apr;60(4):262-8. doi: 10.1369/0022155412438104. Epub 2012 Jan 19. J Histochem Cytochem. 2012. PMID: 22260996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Decorin in the Lens and Ocular Diseases.Cells. 2022 Dec 24;12(1):74. doi: 10.3390/cells12010074. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36611867 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Characterization of an In Vitro Model for Radiation-Induced Fibrosis.Radiat Res. 2018 Mar;189(3):326-336. doi: 10.1667/RR14926.1. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Radiat Res. 2018. PMID: 29351058 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Induced Modifications of the Gene Expression Kinetics of Differentiating Skeletal Muscle Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 8;10(10):e0139520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139520. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26447881 Free PMC article.
-
Oncosuppressive roles of decorin through regulation of multiple receptors and diverse signaling pathways.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Mar 1;322(3):C554-C566. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00016.2022. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35171698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leucine supplementation accelerates connective tissue repair of injured tibialis anterior muscle.Nutrients. 2014 Sep 29;6(10):3981-4001. doi: 10.3390/nu6103981. Nutrients. 2014. PMID: 25268835 Free PMC article.
-
Decorin: A Growth Factor Antagonist for Tumor Growth Inhibition.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:654765. doi: 10.1155/2015/654765. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26697491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Massagué J. (1998) TGF-β signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 753–791 - PubMed
-
- Gray P. C., Bilezikjian L. M., Vale W. (2002) Antagonism of activin by inhibin and inhibin receptors. A functional role for betaglycan. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 188, 254–260 - PubMed
-
- Massagué J., Gomis R. R. (2006) The logic of TGF-βa signaling. FEBS Lett. 580, 2811–2820 - PubMed
-
- Kang J. S., Liu C., Derynck R. (2009) New regulatory mechanisms of TGF-β receptor function. Trends Cell Biol. 19, 385–394 - PubMed
-
- Brandan E., Retamal C., Cabello-Verrugio C., Marzolo M. P. (2006) The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein functions as an endocytic receptor for decorin. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 31562–31571 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

