Mbd3/NURD complex regulates expression of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine marked genes in embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 22196727
- PMCID: PMC3252821
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.054
Mbd3/NURD complex regulates expression of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine marked genes in embryonic stem cells
Abstract
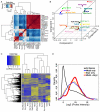
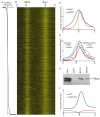
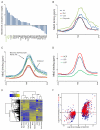
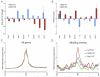
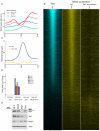
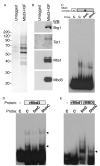
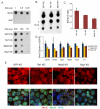
Numerous chromatin regulators are required for embryonic stem (ES) cell self-renewal and pluripotency, but few have been studied in detail. Here, we examine the roles of several chromatin regulators whose loss affects the pluripotent state of ES cells. We find that Mbd3 and Brg1 antagonistically regulate a common set of genes by regulating promoter nucleosome occupancy. Furthermore, both Mbd3 and Brg1 play key roles in the biology of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC): Mbd3 colocalizes with Tet1 and 5hmC in vivo, Mbd3 knockdown preferentially affects expression of 5hmC-marked genes, Mbd3 localization is Tet1-dependent, and Mbd3 preferentially binds to 5hmC relative to 5-methylcytosine in vitro. Finally, both Mbd3 and Brg1 are themselves required for normal levels of 5hmC in vivo. Together, our results identify an effector for 5hmC, and reveal that control of gene expression by antagonistic chromatin regulators is a surprisingly common regulatory strategy in ES cells.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis identifies a functional association of Tet1 and Polycomb repressive complex 2 in mouse embryonic stem cells.Genome Biol. 2013 Aug 29;14(8):R91. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-8-r91. Genome Biol. 2013. PMID: 23987249 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine distribution reveals its dual function in transcriptional regulation in mouse embryonic stem cells.Genes Dev. 2011 Apr 1;25(7):679-84. doi: 10.1101/gad.2036011. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21460036 Free PMC article.
-
Tet1 and 5-hydroxymethylation: a genome-wide view in mouse embryonic stem cells.Cell Cycle. 2011 Aug 1;10(15):2428-36. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.15.16930. Epub 2011 Aug 1. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21750410 Free PMC article.
-
NuRD and pluripotency: a complex balancing act.Cell Stem Cell. 2012 May 4;10(5):497-503. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.04.011. Cell Stem Cell. 2012. PMID: 22560073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of TET proteins and 5-hydroxymethylcytosines in active DNA demethylation and beyond.Cell Cycle. 2011 Aug 15;10(16):2662-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.16.17093. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 21811096 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tet family of 5-methylcytosine dioxygenases in mammalian development.J Hum Genet. 2013 Jul;58(7):421-7. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2013.63. Epub 2013 May 30. J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23719188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chromatin remodeler chd5 is necessary for proper head development during embryogenesis of Danio rerio.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Aug;1849(8):1040-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.06.006. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26092436 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in neurodegenerative diseases.Front Neurosci. 2014 Dec 5;8:397. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00397. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25538551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined deficiency of Tet1 and Tet2 causes epigenetic abnormalities but is compatible with postnatal development.Dev Cell. 2013 Feb 11;24(3):310-23. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2012.12.015. Epub 2013 Jan 24. Dev Cell. 2013. PMID: 23352810 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Changes and Chromatin Reorganization in Brain Function: Lessons from Fear Memory Ensemble and Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 11;23(20):12081. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012081. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36292933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azuara V, Perry P, Sauer S, Spivakov M, Jorgensen HF, John RM, Gouti M, Casanova M, Warnes G, Merkenschlager M, et al. Chromatin signatures of pluripotent cell lines. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:532–538. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
-
- Boyer LA, Plath K, Zeitlinger J, Brambrink T, Medeiros LA, Lee TI, Levine SS, Wernig M, Tajonar A, Ray MK, et al. Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2006;441:349–353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

