Performance of the CareStart™ G6PD deficiency screening test, a point-of-care diagnostic for primaquine therapy screening
- PMID: 22164279
- PMCID: PMC3229584
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028357
Performance of the CareStart™ G6PD deficiency screening test, a point-of-care diagnostic for primaquine therapy screening
Abstract
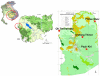
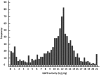
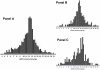
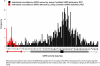
Development of reliable, easy-to-use, rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) to detect glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency at point of care is essential to deploying primaquine therapies as part of malaria elimination strategies. We assessed a kit under research and development called CareStart™ G6PD deficiency screening test (Access Bio, New Jersey, USA) by comparing its performance to quantitative G6PD enzyme activity using a standardized spectrophotometric method ('gold standard'). Blood samples (n = 903) were collected from Cambodian adults living in Pailin province, western Cambodia. G6PD enzyme activities ranged from 0 to 20.5 U/g Hb (median 12.0 U/g Hg). Based on a normal haemoglobin concentration and wild-type G6PD gene, the normal values of G6PD enzymatic activity for this population was 3.6 to 20.5 U/g Hg (95(th) percentiles from 5.5 to 17.2 U/g Hg). Ninety-seven subjects (10.7%) had <3.6 U/g Hg and were classified as G6PD deficient. Prevalence of deficiency was 15.0% (64/425) among men and 6.9% (33/478) among women. Genotype was analyzed in 66 G6PD-deficient subjects and 63 of these exhibited findings consistent with Viangchang genotype. The sensitivity and specificity of the CareStart™ G6PD deficiency screening test was 0.68 and 1.0, respectively. Its detection threshold was <2.7 U/g Hg, well within the range of moderate and severe enzyme deficiencies. Thirteen subjects (1.4%, 12 males and 1 female) with G6PD enzyme activities <2 U/g Hg were falsely classified as "normal" by RDT. This experimental RDT test here evaluated outside of the laboratory for the first time shows real promise, but safe application of it will require lower rates of falsely "normal" results.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency among Yemeni children residing in malaria-endemic areas of Hodeidah governorate and evaluation of a rapid diagnostic test for its detection.Malar J. 2016 Jun 21;15:327. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1372-9. Malar J. 2016. PMID: 27329471 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of Three Quantitative Methods to Estimate G6PD Activity in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, Bangladesh.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 25;12(1):e0169930. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169930. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28121993 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the CareStart™ glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) rapid diagnostic test in the field settings and assessment of perceived risk from primaquine at the community level in Cambodia.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 31;15(1):e0228207. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228207. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32004348 Free PMC article.
-
G6PD deficiency: global distribution, genetic variants and primaquine therapy.Adv Parasitol. 2013;81:133-201. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407826-0.00004-7. Adv Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23384623 Review.
-
Primaquine for reducing Plasmodium falciparum transmission.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;(9):CD008152. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008152.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jun 30;(6):CD008152. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008152.pub3. PMID: 22972117 Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Vivax malaria in pregnancy and lactation: a long way to health equity.Malar J. 2020 Jan 22;19(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12936-020-3123-1. Malar J. 2020. PMID: 31969155 Free PMC article.
-
The challenges of introducing routine G6PD testing into radical cure: a workshop report.Malar J. 2015 Sep 29;14:377. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0896-8. Malar J. 2015. PMID: 26416229 Free PMC article.
-
G6PD deficiency in Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax malaria-infected Cambodian patients.Malar J. 2013 May 28;12:171. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-171. Malar J. 2013. PMID: 23714236 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and distribution of G6PD deficiency: implication for the use of primaquine in malaria treatment in Ethiopia.Malar J. 2019 Oct 7;18(1):340. doi: 10.1186/s12936-019-2981-x. Malar J. 2019. PMID: 31590661 Free PMC article.
-
Costs and Cost-Effectiveness of Plasmodium vivax Control.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016 Dec 28;95(6 Suppl):52-61. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0182. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016. PMID: 28025283 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Malaria elimination. A field manual for low and moderate endemic countries, WHO, Geneva. 2007. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2007/9789241596084_eng.pdf.
-
- Noedl H, Se Y, Schaecher K, Smith BL, Socheat D, et al. Evidence of artemisinin-resistant malaria in western Cambodia. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2619–2620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

