Anti-aquaporin-4 antibody-positive neuromyelitis optica presenting with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion as an initial manifestation
- PMID: 22125526
- PMCID: PMC3224522
- DOI: 10.1159/000334129
Anti-aquaporin-4 antibody-positive neuromyelitis optica presenting with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion as an initial manifestation
Abstract
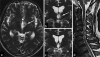
The distribution of neuromyelitis optica (NMO)-characteristic brain lesions corresponds to sites of high aquaporin-4 (AQP4) expression, and the brainstem and hypothalamus lesions that express high levels of AQP4 protein are relatively characteristic of NMO. The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) is one of the important causes of hyponatremia and results from an abnormal production or sustained secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH). SIADH has been associated with many clinical states or syndromes, and the hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal system regulates the feedback control system for ADH secretion. We report the case of a 63-year-old man with NMO, whose initial manifestation was hyponatremia caused by SIADH. Retrospective analysis revealed that the serum anti-AQP4 antibody was positive, and an MRI scan showed a unilateral lesion in the hypothalamus. SIADH recovered completely with regression of the hypothalamic lesion. As such, NMO should even be considered in patients who develop SIADH and have no optic nerve or spinal cord lesions but have MRI-documented hypothalamic lesions.
Keywords: Anti-aquaporin-4 antibody; Hypothalamus; Neuromyelitis optica; Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion associated with seronegative neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder.Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2017 Mar;36(1):100-104. doi: 10.23876/j.krcp.2017.36.1.100. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28393003 Free PMC article.
-
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion in patients with aquaporin-4 antibody.J Neurol. 2015 Jan;262(1):101-7. doi: 10.1007/s00415-014-7537-y. Epub 2014 Oct 15. J Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25315741
-
[Neuromyelitis optica with syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone and hypersomnia associated with bilateral hypothalamic lesions: a case report].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2011 Aug;51(8):599-602. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.51.599. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2011. PMID: 21878727 Japanese.
-
Hyponatremia in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: Literature review.Acta Neurol Scand. 2018 Jul;138(1):4-11. doi: 10.1111/ane.12938. Epub 2018 Apr 14. Acta Neurol Scand. 2018. PMID: 29654708 Review.
-
Neuromyelitis optica, aquaporin-4 antibodies, and neuroendocrine disorders.Handb Clin Neurol. 2021;181:173-186. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-820683-6.00013-0. Handb Clin Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34238456 Review.
Cited by
-
MRI Patterns Distinguish AQP4 Antibody Positive Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder From Multiple Sclerosis.Front Neurol. 2021 Sep 9;12:722237. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.722237. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34566866 Free PMC article.
-
MOG-IgG in NMO and related disorders: a multicenter study of 50 patients. Part 2: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, radiological and laboratory features, treatment responses, and long-term outcome.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Sep 27;13(1):280. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0718-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27793206 Free PMC article.
-
Pearls & Oy-sters: Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion Presenting as Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Flare.Neurology. 2023 Jul 25;101(4):e455-e458. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000207178. Neurology. 2023. PMID: 37487758 Free PMC article.
-
Conventional and advanced imaging in neuromyelitis optica.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014 Aug;35(8):1458-66. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3592. Epub 2013 Jun 13. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014. PMID: 23764723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relapse Patterns in NMOSD: Evidence for Earlier Occurrence of Optic Neuritis and Possible Seasonal Variation.Front Neurol. 2020 Jun 16;11:537. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00537. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32612571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wingerchuk DM, Lennon VA, Lucchinetti CF, Pittock SJ, Weinshenker BG. The spectrum of neuromyelitis optica. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:805–815. - PubMed
-
- Pittock SJ, Weinshenker BG, Lucchinetti CF, Wingerchuk DM, Corboy JR, Lennon VA. Neuromyelitis optica brain lesions localized at sites of high aquaporin 4 expression. Arch Neurol. 2006;63:964–968. - PubMed
-
- Nakashima I, Fujihara K, Miyazawa I, Misu T, Narikawa K, Nakamura M, Watanabe S, Takahashi T, Nishiyama S, Shiga Y, Sato S, Weinshenker BG, Itoyama Y. Clinical and MRI features of Japanese patients with multiple sclerosis positive for NMO-IgG. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006;77:1073–1075. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schwartz WB, Bennett W, Curelop S, Bartter FC. A syndrome of renal sodium loss and hyponatremia probably resulting from inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. American Journal of Medicine. 1957;23:529–542. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

