The laforin-malin complex negatively regulates glycogen synthesis by modulating cellular glucose uptake via glucose transporters
- PMID: 22124153
- PMCID: PMC3266598
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.06353-11
The laforin-malin complex negatively regulates glycogen synthesis by modulating cellular glucose uptake via glucose transporters
Abstract
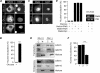
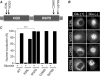
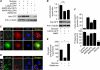
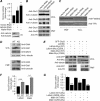
Lafora disease (LD), an inherited and fatal neurodegenerative disorder, is characterized by increased cellular glycogen content and the formation of abnormally branched glycogen inclusions, called Lafora bodies, in the affected tissues, including neurons. Therefore, laforin phosphatase and malin ubiquitin E3 ligase, the two proteins that are defective in LD, are thought to regulate glycogen synthesis through an unknown mechanism, the defects in which are likely to underlie some of the symptoms of LD. We show here that laforin's subcellular localization is dependent on the cellular glycogen content and that the stability of laforin is determined by the cellular ATP level, the activity of 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase, and the affinity of malin toward laforin. By using cell and animal models, we further show that the laforin-malin complex regulates cellular glucose uptake by modulating the subcellular localization of glucose transporters; loss of malin or laforin resulted in an increased abundance of glucose transporters in the plasma membrane and therefore excessive glucose uptake. Loss of laforin or malin, however, did not affect glycogen catabolism. Thus, the excessive cellular glucose level appears to be the primary trigger for the abnormally higher levels of cellular glycogen seen in LD.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Deciphering the role of malin in the lafora progressive myoclonus epilepsy.IUBMB Life. 2012 Oct;64(10):801-8. doi: 10.1002/iub.1072. Epub 2012 Jul 20. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 22815132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lafora disease proteins laforin and malin negatively regulate the HIPK2-p53 cell death pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Aug 14;464(1):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.018. Epub 2015 Jun 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26102034
-
Interdependence of laforin and malin proteins for their stability and functions could underlie the molecular basis of locus heterogeneity in Lafora disease.J Biosci. 2015 Dec;40(5):863-71. doi: 10.1007/s12038-015-9570-0. J Biosci. 2015. PMID: 26648032
-
Lafora disease proteins malin and laforin are recruited to aggresomes in response to proteasomal impairment.Hum Mol Genet. 2007 Apr 1;16(7):753-62. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm006. Epub 2007 Mar 2. Hum Mol Genet. 2007. PMID: 17337485
-
Lafora disease: Current biology and therapeutic approaches.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022 Apr;178(4):315-325. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2021.06.006. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022. PMID: 34301405 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuromuscular junction dysfunction in Lafora disease.Dis Model Mech. 2024 Oct 1;17(10):dmm050905. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050905. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Dis Model Mech. 2024. PMID: 39301689 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the role of malin in the lafora progressive myoclonus epilepsy.IUBMB Life. 2012 Oct;64(10):801-8. doi: 10.1002/iub.1072. Epub 2012 Jul 20. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 22815132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lafora Disease: A Ubiquitination-Related Pathology.Cells. 2018 Jul 26;7(8):87. doi: 10.3390/cells7080087. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30050012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of serum/glucocorticoid-induced kinase 1 (SGK1) underlies increased glycogen levels, mTOR activation, and autophagy defects in Lafora disease.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Dec;24(24):3776-86. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-05-0261. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 24131995 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of pancreatic fat: The Multiethnic Cohort Adiposity Phenotype Study.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 30;16(7):e0249615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249615. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34329319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker M, Newman S, Ismail-Beigi F. 1996. Stimulation of GLUT1 glucose transporter expression in response to inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation: role of reduced sulfhydryl groups. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 121:165–170 - PubMed
-
- Bell B, Xing H, Yan K, Gautam N, Muslin AJ. 1999. KSR-1 binds to G-protein βγ subunits and inhibits βγ-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 274:7982–7986 - PubMed
-
- Boer P, Sperling O. 2004. Modulation of glycogen phosphorylase activity affects 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate availability in rat hepatocyte cultures. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 23:1235–1239 - PubMed
-
- Chan EM, et al. 2004. Laforin preferentially binds the neurotoxic starch-like polyglucosans, which form in its absence in progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 13:1117–1129 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
