Biodegradable nanoparticles are excellent vehicle for site directed in-vivo delivery of drugs and vaccines
- PMID: 22123084
- PMCID: PMC3238292
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-55
Biodegradable nanoparticles are excellent vehicle for site directed in-vivo delivery of drugs and vaccines
Abstract
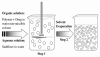
Biodegradable nanoparticles (NPs) are gaining increased attention for their ability to serve as a viable carrier for site specific delivery of vaccines, genes, drugs and other biomolecules in the body. They offer enhanced biocompatibility, superior drug/vaccine encapsulation, and convenient release profiles for a number of drugs, vaccines and biomolecules to be used in a variety of applications in the field of medicine. In this manuscript, the methods of preparation of biodegradable NPs, different factors affecting optimal drug encapsulation, factors affecting drug release rates, various surface modifications of nanoparticles to enhance in-vivo circulation, distribution and multimodal functionalities along with the specific applications such as tumor targeting, oral delivery, and delivery of these particles to the central nervous system have been reviewed.
Figures

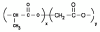
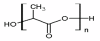
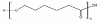
Similar articles
-
Overview of the preparation of organic polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery based on gelatine, chitosan, poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolic acid) and polyalkylcyanoacrylate.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014 Jun 1;118:154-63. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.03.017. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014. PMID: 24769392 Review.
-
Preparation and properties of nanosized biodegradable polymer capsules.J Oleo Sci. 2011;60(11):569-73. doi: 10.5650/jos.60.569. J Oleo Sci. 2011. PMID: 22027022
-
Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone Loaded and Chitosan Engineered Polymeric Nanoparticles: Towards Effective Delivery of Neuropeptides.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016 May;16(5):5324-32. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2016.12431. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27483926
-
Synthesis of biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles and their controlled drug delivery for tuberculosis.J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2011 Feb;7(1):150-1. doi: 10.1166/jbn.2011.1244. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21485846
-
Biodegradable polymeric nanocarriers for pulmonary drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008 Jun;5(6):629-39. doi: 10.1517/17425247.5.6.629. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2008. PMID: 18532919 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Polymeric Materials for the Advancement of Regenerative Medicine.J Funct Biomater. 2021 Feb 20;12(1):14. doi: 10.3390/jfb12010014. J Funct Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33672492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Chemical Biology of Mitochondria Targeting.Front Chem. 2021 May 3;9:683220. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.683220. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34012953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular Drug Delivery: Role of Degradable Polymeric Nanocarriers for Ophthalmic Application.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 19;19(9):2830. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092830. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30235809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymeric Nanoparticles in Gene Therapy: New Avenues of Design and Optimization for Delivery Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Apr 25;11(4):745. doi: 10.3390/polym11040745. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31027272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-CRLF2 Antibody-Armored Biodegradable Nanoparticles for Childhood B-ALL.Part Part Syst Charact. 2013 Apr;30(4):355-364. doi: 10.1002/ppsc.201200125. Part Part Syst Charact. 2013. PMID: 23976822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu T, Zhang N, Nichols HL, Shi D, Wen X. Modification of nanostructured materials for biomedical applications. Materials Science and Engineering: C. 2007;27(3):579–594.
-
- Mohanraj VJ, Chem Y. Nanoparticles-A Review. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 2006;5(1):561–573.
-
- Liu Y, Miyoshi H, Nakamura M. Nanomedicine for drug delivery and imaging: A promising avenue for cancer therapy and diagnosis using targeted functional nanoparticles. International Journal of Cancer. 2007;120(12):2527–2537. - PubMed
-
- van Vlerken LE, Amiji MM. Multi-functional polymeric nanoparticles for tumour-targeted drug delivery. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery. 2006;3(2):205–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

